WNDNovember 07, 2023
Tag: ADC , antibody , inhibitors
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are a class of drugs composed of antibodies targeting tumor antigens and a variable number of small molecule toxins linked through connectors. The antibody component functions in targeted localization, achieving the targeted aggregation of the drug. Currently, the development primarily focuses on mature monoclonal antibodies, while ADC drugs with bispecific/multispecific antibodies are still in the early exploration stage. The small molecule toxins mainly consist of chemotherapeutic agents with tumor-killing effects, categorized as DNA inhibitors, microtubule inhibitors, topoisomerase inhibitors, etc., with microtubule inhibitors being the primary type at present. The connectors are divided into degradable and non-degradable types, with degradable connectors capable of disintegrating upon entering cells, releasing toxin molecules and enhancing their tumor-killing effects, gradually becoming the mainstream direction of development. At present, a total of 15 ADC drugs have been approved for marketing globally, and this article will systematically inventory the marketed drugs one by one.
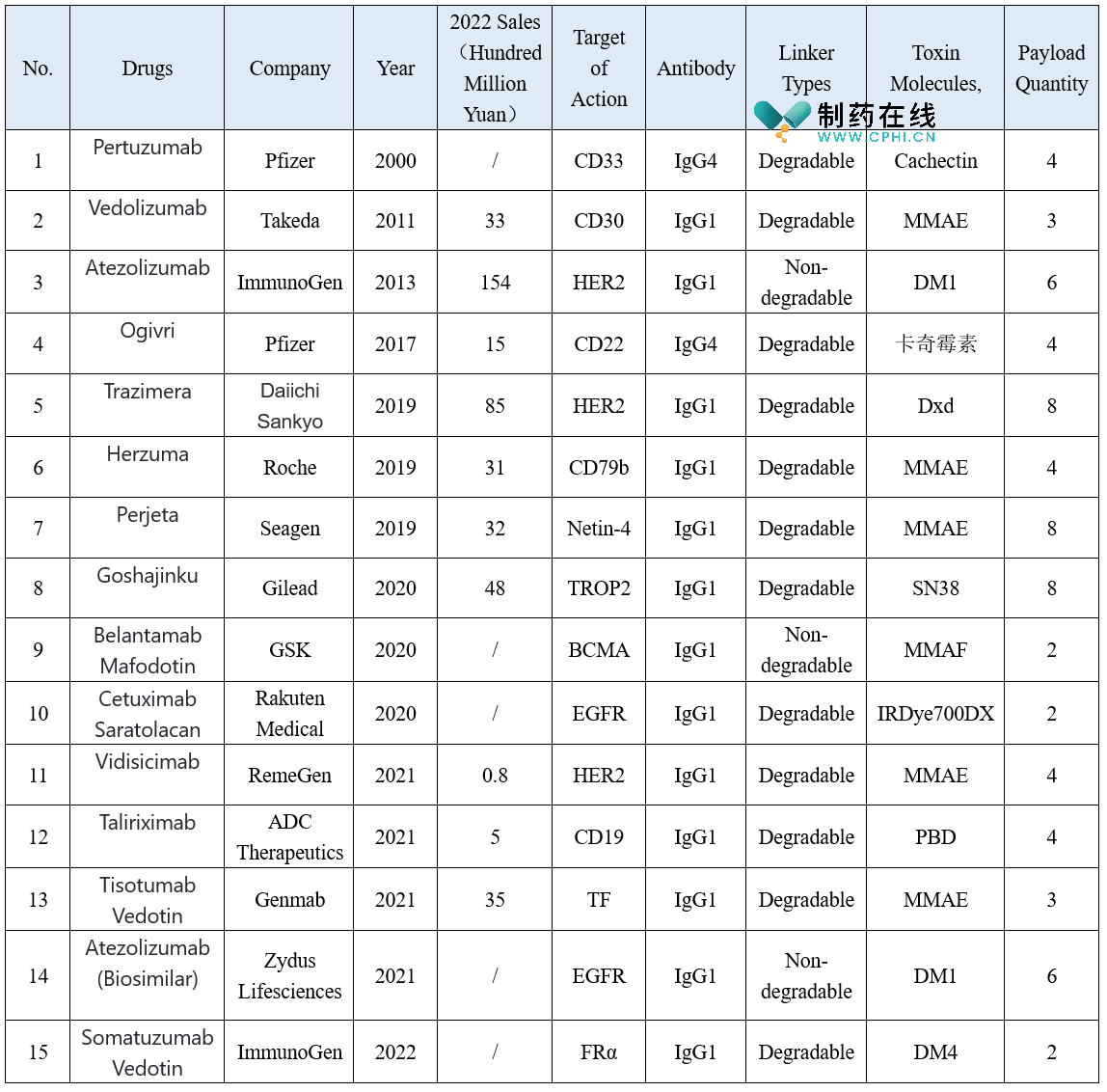
Gemtuzumab ozogamicin is the first ADC drug approved by the FDA, targeting CD33. It is a humanized IgG4 antibody conjugated with a calicheamicin derivative through disulfide bonds. This drug can specifically bind to leukemia cells expressing CD33, leading to internalization and subsequent hydrolysis of the linker, releasing calicheamicin into the cell nucleus where it binds to DNA, causing double-strand breaks and ultimately leading to cell death. It was intended for the treatment of relapsed AML in patients aged 60 and above who were not fit for other chemotherapy, but due to lack of significant clinical efficacy evidence and substantial hepatotoxicity, it has been withdrawn from the market.
Brentuximab vedotin is an ADC drug targeting CD30, consisting of a protease-cleavable linker that maintains stability in the bloodstream and releases MMAE upon internalization into CD30-expressing cells, leading to targeted cell death. It is used for the treatment of systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma, classical Hodgkin lymphoma, primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma, or mycosis fungoides. It was approved for marketing domestically in 2020 and was included in the national medical insurance directory in 2022. The price was adjusted to 7202 yuan/50ml, representing a 54% reduction, effectively reducing the financial burden on lymphoma patients.
Trastuzumab emtansine is a HER2-targeting ADC drug containing emtansine, which is irreversibly conjugated to trastuzumab through a stable linker, exerting its cytotoxic effect on tumor cells. It is indicated for the treatment of HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer in patients previously treated with trastuzumab and a taxane, either separately or in combination. It was approved for marketing domestically in 2020, making it the first ADC drug to be marketed in the country. In 2022, global sales exceeded 15 billion yuan, ranking it at the top of the ADC drug market, demonstrating significant clinical treatment advantages.
Inotuzumab ozogamicin is an ADC drug targeting CD22, composed of inotuzumab and calicheamicin derivative linked by a degradable linker. It is used for the treatment of relapsed or refractory B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adults. It was launched in China in 2021, and clinical results show that compared to standard therapy (standard intensive chemotherapy), inotuzumab ozogamicin achieves higher complete remission rates, longer progression-free survival, and overall survival.
Trastuzumab deruxtecan is also a HER2-targeting ADC drug, composed of trastuzumab and a deruxtecan derivative linked by a degradable linker. It is indicated for the treatment of unresectable or metastatic HER2-positive adult breast cancer patients who have received one or more prior anti-HER2 therapies. It was approved for marketing in China in February this year, and in July, it received domestic approval for a new indication. As a highly anticipated new generation ADC drug, its clinical benefits have been fully validated. Data from the first head-to-head comparison clinical trial between ADC drugs showed that the median progression-free survival in the trastuzumab deruxtecan group was as long as 28.8 months, which is 4.2 times that of the trastuzumab emtansine group, pushing the benefits of second-line anti-HER2 treatment to new heights.
Vedotin is a monoclonal antibody that targets the CD79b receptor. The monoclonal antibody binds to the cell surface CD79b with high affinity and selectivity, followed by lysosomal protease cleavage of the linker, releasing MMAE. This inhibits cell division and induces apoptosis, thereby killing malignant B lymphocytes. It is used in untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in adults. It was approved for market launch in China in January of this year. Clinical research data shows that compared to standard treatment regimens, it significantly improves progression-free survival, reducing the relative risk of disease progression, relapse, or death by 27%.
Vinutuzumab is a first-in-class ADC drug that directly targets Nectin-4. It is used to treat locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma patients who have previously received PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors and platinum-containing chemotherapy. It is currently in the application phase for market approval in China.
Goshajutuzumab is the first ADC drug targeting TROP2. The monoclonal antibody is linked to approximately 8 highly potent cytotoxic drug SN-38, providing stable antitumor effects. It is used for the treatment of advanced triple-negative breast cancer. It was approved for market launch in China in 2022, bringing a new treatment option for Chinese patients with advanced triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
Belantamab Mafodotin targets BCMA and is an ADC consisting of a monoclonal antibody linked to the microtubule inhibitor MMAF, which has high cytotoxicity. It cannot be used directly, but must be delivered in ADC form, concentrating it directly on tumor cells. It is used for the treatment of multiple myeloma.
Cetuximab Saratolacan targets the EGFR and consists of the cetuximab monoclonal antibody linked to IRDye700DX. It can target the epidermal growth factor receptor and is the world's first approved photoimmunotherapy drug for head and neck cancer. After binding to the drug and cancer cells, near-infrared light is irradiated onto the patient, activating the drug to kill the cancer cells.
Vidyutuzumab is the first domestically developed ADC drug targeting the HER2 receptor. It has a milestone significance in the domestic ADC drug field. It is used for the treatment of HER2-overexpressing locally advanced or metastatic gastric cancer (including gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma) patients who have received at least 2 systemic chemotherapies. It entered the national medical insurance catalog in 2022, with a significantly reduced price of 3800 yuan/60mg, effectively reducing the burden on patients.
Talantuzumab is the world's first ADC drug targeting CD19. After entering the cell, it releases pyrrole and benzodiazepine dimer, inhibiting DNA replication, leading to tumor cell death. It is used as a monotherapy for adult patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma who have previously received at least second-line systemic treatment. In July of this year, it was submitted for market approval in China by LengLu Pharmaceuticals and ADC Therapeutics, and is also the first domestically declared ADC targeting CD19.
Tisotumab Vedotin targets the TF protein on the cell surface. After drug cleavage, it releases MMAE, disrupting the microtubule network for tumor cell replication, leading to cell cycle arrest and tumor cell death. It is used for the treatment of recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer during or after chemotherapy, with clinical trial data showing an objective response rate of 24% and a median progression-free survival of 4.2 months.
This drug is a biosimilar of enmetuzumab vedotin, as introduced above.
Sotiguzumab is the world's first antibody-drug conjugate targeting folate receptor alpha (FRα). It received accelerated approval from the FDA last December for the treatment of platinum-resistant ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer in adult patients who are FRα-positive and have previously received 1-3 lines of systemic therapy. Its Greater China rights have been transferred to Huadong Medicine, and it has obtained priority review qualification from the Center for Drug Evaluation in China. In August of this year, Huadong Medicine officially launched a real-world study of platinum-resistant ovarian cancer in Boao, Hainan.
The concept of ADC drugs was proposed as early as a hundred years ago, but due to high technological barriers, development has been slow. However, in recent years, with the rapid development of conjugation technologies, the industry has entered the fast lane of development and has become the most hotly contested field in biomedicine. Capital continues to pour into this field, with over 120 financing events and a total financing amount of over 87 billion RMB in the past five years. Leading domestic and foreign companies as well as biotechs have been increasing their presence in this field, and research interest continues to rise. However, this has also brought about the clustering of targets in this field and homogenized research. How to differentiate in the future will be the focus of consideration for enterprises.


Contact Us
Tel: (+86) 400 610 1188
WhatsApp/Telegram/Wechat: +86 13621645194
+86 15021993094
Follow Us:




 Pharma Sources Insight July 2025
Pharma Sources Insight July 2025


