PharmaSources/YuntianFebruary 19, 2021
NMN, i.e., nicotinamide mononucleotide (Fig. 1), is a reaction product of nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT). NMN has attracted great attention and the demand for it as an API has been increasing in recent years, as it has been found to improve cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, diabetes, obesity, and aging.
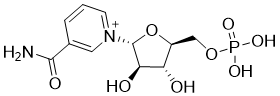
Fig. I NMN Structural Formula
NMN is mainly prepared by chemical synthesis and enzymatic synthesis. Enzymatic synthesis, compared to chemical synthesis, is considered to be a green and environmentally friendly method as it does not produce organic solvent residues or require chirality consideration.
Back in 1957, Jack et al. elucidated the pathway of β-NMN production in the body by using phosphoribosylpyrophosphate (PRPP) and nicotinamide as raw materials for the enzymatic synthesis of β-NMN in erythrocyte extracts. The synthesis route is shown in Fig. 2: nicotinamide and PRPP are catalyzed by NAMPT (or NAMPRT) to produce NMN and pyrophosphate (PPi). Furthermore, nicotinamide riboside (NR) is phosphorylated to produce NMN as catalyzed by nicotinamide riboside kinase (NRK).
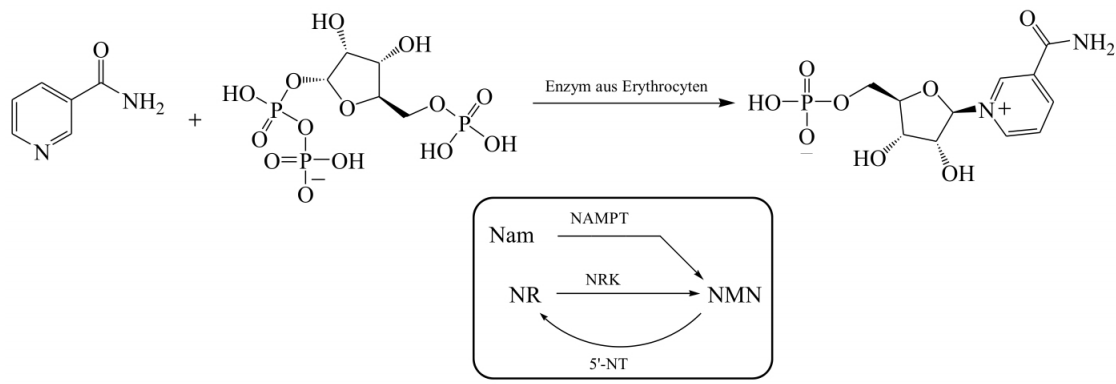
Fig. II Enzymatic Synthesis Route of Jack et al.
Chinese researchers and medical surgical supply companies have done much research on the enzymatic synthesis of NMN. Fu Rongzhao et al. synthesized NMN using a combination of three enzymes, hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT), xanthine oxidase, and NAMPT, with pyrophosphate, nicotinamide, and inosinic acid as substrates. The conversion rate of this reaction could reach 80% to 100%, however, the by-product xanthine produced in the reaction would inhibit the NAMPT enzyme, which needs to be degraded by xanthine oxidase, making the reaction system complex.
Subsequently, Fu Rongzhao et al. synthesized NMN using three enzymes: AMP nucleosidase, PRS, and NAMPT, with phosphoric acid, nicotinamide, and inosinic acid as substrates. The reaction had a high conversion rate, however, the AMP nucleosidase used was not much studied, and it was difficult to find a suitable enzyme for production using this process.
Furthermore, Fu Rongzhao et al. used a multi-enzyme combination of ribose kinase, ribose-phosphate pyrophosphokinase, and NAMPT to synthesize NMN from the raw materials: nicotinamide, adenosine triphosphate, and ribose, which can be fed in a one-step or a distributed manner (firstly, ribose reacts with adenosine triphosphate to obtain PRPP, and then add nicotinamide to obtain NMN). The one-step feeding has the advantages of short reaction time and simple operation, while distributed feeding has the advantage of thorough reaction. The conversion rate of this reaction could also reach 80% to 100%, the ribose kinase and ribose-phosphate pyrophosphokinase used are more deeply studied, and the reaction process is clear.
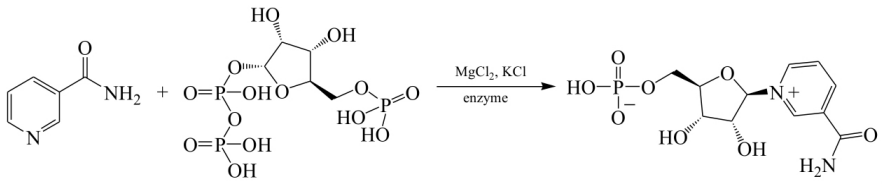
Fig. III Enzymatic Synthesis Route of Fu Rongzhao, et al.
In 2018 (Fig. 3), Fu Rongzhao et al. applied for an international patent (WO, 2018023206 [P]. 2018-02-08), which artificially constructs various NAMPT mutants with high catalytic activity using a gene site-directed mutagenesis method, and then catalyzes nicotinamide and PRPP to synthesize NMN with these highly active mutants. This process has high enzymatic activity and high industrial application value.
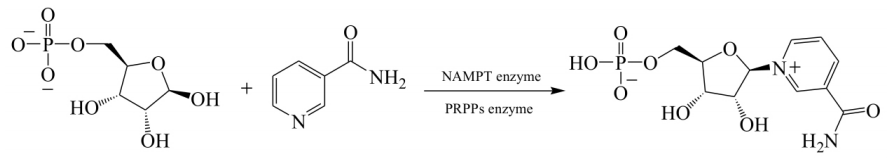
Fig. IV Enzymatic Synthesis Route of Zhu Wei
In 2018, Zhu Wei et al. used D-ribose 5-phosphate and nicotinamide as raw materials to achieve efficient NMN synthesis in one step with NMN concentration up to 13.3 g/L and conversion rate up to 99.5% using whole-cell catalysis of genetically engineered bacteria cured containing PRPP synthetase (PRS) and NAMPT in the presence of ATP. This process has many advantages low cost, simple production process, and recyclable cells, giving it an edge in cost saving.
To sum up, researchers have been developing a better process for NMN, and enzymatic synthesis, as a green and efficient synthesis method, plays an essential role in the preparation of NMN. We can be sure that with the continuous improvement of biotechnology and the research on the NMN enzymatic process, better NMN enzymatic processes will continue to emerge in the future.
References:
1. Progress in Synthsis of β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide, 2020;
2. Advance in Synthesis of β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide, 2020.
3. Patent: WO, 2018023206[P]. 2018-02-08.
4. Patent: CN108949865[P]. 2018-12-07.
5. Patent: CN107889505A[P],2018-04-06.
6. Patent: CN108026535A[P],2018-05-11.
7. Patent: CN108026130A[P],2018-05-11.
Yuntian, Ph.D. in medicinal chemistry, is mainly engaged in small molecule drug research, especially good at small molecule drug synthesis process and later stage drug development research. He has completed the synthesis and activity evaluation of multiple anti-cancer drug molecules.


Contact Us
Tel: (+86) 400 610 1188
WhatsApp/Telegram/Wechat: +86 13621645194
+86 15021993094
Follow Us:




 Pharma Sources Insight July 2025
Pharma Sources Insight July 2025


