Neeta RatanghayraMarch 18, 2021
Tag: biosimilars , FDA , EMA
2020 has been a tough year. The pandemic posed an array of challenges to the healthcare system and the global biopharmaceutical industry both rose to the challenges and seized opportunities.
Biosimilars offer the potential for more treatment options and affordable alternatives. Experts suggest that the broader adoption of biosimilars could lead to greater competition, ultimately reducing medical and surgical supplies costs and enabling wider access to life-saving drugs.
Year 2020 - Low approvals, but significant advances
The year 2020 saw just three biosimilar approvals from the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA), while the European Medicines Agency (EMA) approved nine products.
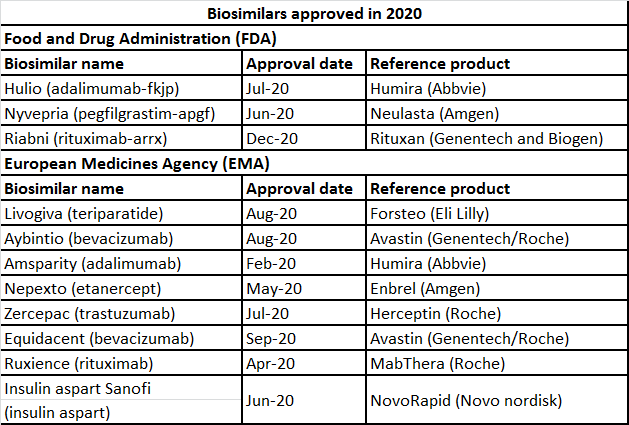
The number of biosimilars approved in 2020 was low; however, there were great advances in clinical testing of new biosimilars, collaborations/deals, and exploration of innovative ways to implement biosimilars as a cost-saving strategy.
Biosimilars in China – An overview
The United States and Europe together account for more than 90% of biosimilars sales; however, there has been tremendous progress in the biopharmaceutical markets in East Asian countries such as China.
There is a huge unmet medical need for affordable biologics in China. Biosimilar drugs appear to be the best alternate solution for improving access to life-saving biologics.
In February 2019, China’s National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) approved the country’s first-ever biosimilar product, Hanlikang/HLX01 (rituximab), a monoclonal antibody developed by Henlius Biopharmaceutical. Hanlikang/HLX01 references Genentech and Biogen’s Rituxan (rituximab) and is indicated for non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. This approval flagged off the biosimilar boom in China. The latest to join the list of approved biosimilars in China is adalimumab biosimilar, HLX03, developed by Henlius Biotech. The product was approved by NMPA on 7 December 2020.
Below is the list of biosimilars approved in China.
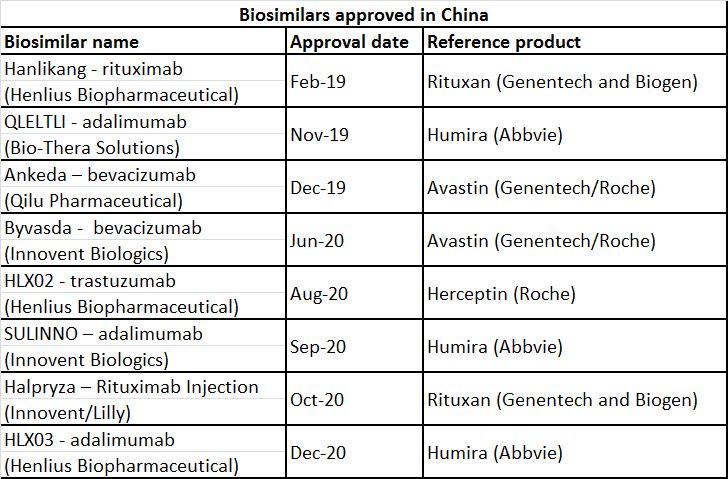
Despite the late start, it has been reported that China has approved more than 200 clinical trials for biosimilars and this is reflected by an increasing pace of approvals and other activity starting in the later part of 2019.
Countering biosimilar disparagement and misinformation
Despite the noted benefits and cost-saving opportunity, biosimilar use is still limited in some healthcare systems because they are not well understood by many health care professionals and patients. There are several different types of disparagement and misinformation related to biosimilars, which hampers their acceptance and market penetration.
As per an opinion piece published in the journal BioDrugs in 2020, disparagement and misinformation about biosimilars can be countered by balanced educational outreach across stakeholders, appropriate regulatory oversight, and use of enforcement powers already granted to government agencies.
Regulatory Challenges for Biosimilars 2020 - WHO Survey of 20 countries
Despite progress with many aspects of the development of biologicals and especially biosimilars, the diversity of regulatory frameworks has presented significant challenges in many countries. A recent WHO survey, which included 20 countries, revealed four main challenges with biosimilars.
· Unavailability or insufficient reference products in particular countries
· Lack of resources
· Problems with the quality of some biosimilars
· Difficulties with interchangeability and naming of biosimilars
The authors recommended potential solutions, noting that resolving these challenges will require cooperation between regulatory authorities in different countries. Their proposed solutions included
· Exchanging information on biologics with other regulatory authorities
· Avoiding unnecessary duplication of studies by accepting foreign-licensed and -sourced reference products
· Relying on approvals from other regulatory authorities or using joint review to facilitate approval of biosimilars
· Reassessing products approved before the biosimilar regulatory framework was in place
· Establishing regulatory oversight for good pharmacovigilance
The road ahead
Experts suggest that the coming years will witness a modest level of biosimilar development. Each biologic has anywhere from one to three candidates in Phase 1 to preregistration, with many in discovery/preclinical development. Apart from this, most biologics with patent expiring in the next five years (2020 to 2025) earn less than $100 million in sales per year, which may impede the commercial opportunity.
Another regulatory debate looming the biosimilar space is whether comparative efficacy trials must be required for approval of all biosimilar products. As per a study published in JAMA in October 2020, comparative efficacy trials for biosimilar products are as rigorous as and often larger, longer, and more costly than many pivotal trials for initial approval of new molecular entities, in contrast to trials for most small-molecule generic drugs, which compare plasma concentrations over time in healthy volunteers. This fact is vital for companies aiming to develop a biosimilar candidate, who should assure that their candidates, once approved, will still be relevant on the market and not be replaced by a next-generation version of the originator.
Biologics have transformed the way hard-to-treat patients are managed. Biosimilars can stimulate market competition and have the potential to expand patient access to life-saving biologics. However, the benefits of biosimilars will only be determined once they are more widely available in the market and used in clinical practice.
References
1. Kang HN, Thorpe R, Knezevic I, et al. Regulatory challenges with biosimilars: an update from 20 countries [published online ahead of print, 2020 Nov 21]. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2020;10.1111/nyas.14522.
2. Cohen HP, McCabe D. The Importance of Countering Biosimilar Disparagement and Misinformation. BioDrugs. 2020;34(4):407-414.
3. Biosimilars in China. 2019. Available at: https://www.parexel.com/news-events-resources/blog/biosimilars-china. Accessed: 11 Jan 2020.
4. CfB Board Members Reflect on Year in Biosimilars. 2020. Available at: https://www.centerforbiosimilars.com/view/cfb-board-members-reflect-on-year-in-biosimilars. Accessed: 11 Jan 2020.
5. Biosimilar Business Roundup: October 2020. Available at: https://www.centerforbiosimilars.com/view/biosimilar-business-roundup-october-2020. Accessed: 11 Jan 2020.
6. From "Musty Towel" To "Golden Age:" Biosimilars In 2021 And Beyond. https://www.biosimilardevelopment.com/doc/from-musty-towel-to-golden-age-biosimilars-in-and-beyond-0002. Accessed: 11 Jan 2020.
7. 2019 Ends and 2020 Begins with a Flurry of Biosimilar Activity in East Asian Markets. https://www.biosimilarsip.com/2020/02/24/2019-ends-and-2020-begins-with-a-flurry-of-biosimilar-activity-in-east-asian-markets/. Accessed: 11 Jan 2020.
About the Author:
Neeta Ratanghayra is a freelance medical writer, who creates quality medical content for Pharma and healthcare industries. A Master’s degree in Pharmacy and a strong passion for writing made her venture into the world of medical writing. She believes that effective content forms the media through which innovations and developments in pharma/healthcare can be communicated to the world."


Contact Us
Tel: (+86) 400 610 1188
WhatsApp/Telegram/Wechat: +86 13621645194
Follow Us:




 Pharma Sources Insight January 2025
Pharma Sources Insight January 2025


