PharmaSourcesMarch 27, 2024
Tag: Cloud Endoscopy System , NTT , Olympus
Cloud endoscopy system using NTT's high-speed, low-latency IOWN APN technology
● NTT's IOWN APN technology and Olympus' advanced technology for endoscopes will be utilized in a demonstration experiment of a cloud endoscopy system that enables real-time image processing of endoscopes on the cloud.
● Through this demonstration experiment, the two companies will establish a reference model for the commercialization of a cloud endoscopy system and contribute to overcoming current limitations of endoscope processing performance and improving maintainability, as well as flexible and rapid response to the market.
NTT Corporation (NTT) and Olympus Corporation (Olympus) today announce that the two companies have jointly begun a demonstration experiment of a cloud endoscopy system that enables image processing on the cloud.
This cloud endoscopy system utilizes Olympus' advanced technology for endoscopes to perform image processing, which has been conventionally processed within the endoscopic equipment, on a remote cloud. This has been difficult to achieve with conventional network technology. NTT's IOWN APN technology1,2 makes it possible to process images in real-time on the cloud. Through this demonstration experiment, the two companies will establish a reference model for the commercialization of the cloud endoscopy system, overcome the current limitations of processing performance of endoscopic equipment, improve maintainability, and provide a flexible and rapid market response to the market.
An endoscope is a medical device in which a flexible tube is inserted into the natural openings of the body to perform an examination and obtain tissue samples. Instances where endoscopes can be utilized are increasing year by year due to the equipment’s low level of invasiveness and high level of safety, and the technology is becoming increasingly sophisticated.
When the endoscope was first introduced, it was a revolutionary device that allowed users to view the inside of the body in real time. Since then, it has progressed even further by supporting highdefinition images, introducing Narrow Band Imaging (NBI) using optical technology, and enabling the collection of samples simultaneously with observation. Recently, advanced support functions have been introduced, such as displaying potential lesions to the operator from the images taken by the endoscope, contributing to the early detection of lesions with greater safety and certainty.
Currently, endoscopes have performance and maintenance limitations. In addition, it is expected that more cases in the future will require flexible feature improvements and updates based on new user needs, such as real-time remote diagnosis and treatment. Therefore, there is discussion on cloud computing endoscopes, in which some functions with a high processing load, such as image processing, can be done in the cloud.
By sharing the processing load with GPUs on the cloud built-in data centers, users can receive the latest functions through software updates on the cloud and enable real-time remote diagnosis and treatment by sharing video information among multiple hospitals.
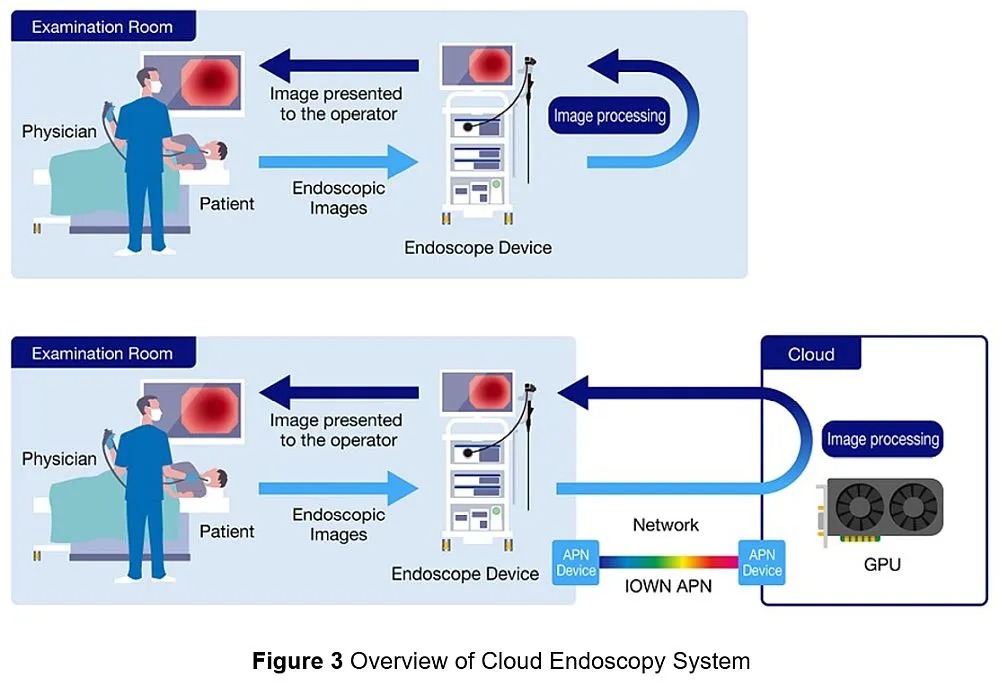
In addition to transitioning existing systems to the cloud, major network-related technical challenges include:
Realizing a high-speed, low-latency network with no delay between the endoscope and the cloud. Conventional networks require a long data transfer time which is unfavorable for the physicians.
Ensuring the high-quality connectivity required for medical endoscopes by promptly detecting abnormalities, such as network failures that would make the cloud unavailable, and providing minimum functions locally in such cases (fallback function).
Implementing advanced security measures on the data transfer path that are difficult even for quantum computers to decode to transmit information safely and accurately.
To realize a cloud endoscopy system, NTT and Olympus have started demonstration experiments centered on IOWN APN to solve technical problems in the network. In this demonstration experiment, the companies will construct an experimental environment in which an actual endoscope and a GPU server are connected by IOWN APN, using it as a starting point to carry out the following verifications:
Verify that the processing delay associated with the cloud does not occur by connecting the endoscope and the server simulating the cloud via an optical transmission path with high speed and low latency.
Verify that the system can achieve the high reliability and availability required for medical devices, including fallback in the event of a network failure.
Verify that information security can be ensured by encrypting information between the endoscope and the cloud using secure optical transport network technology3, which is difficult to attack even using quantum computers.
Based on the knowledge gained from the demonstration experiment, NTT and Olympus will jointly consider the commercialization of the cloud endoscopy system. Furthermore, NTT will establish a reference model for a network for medical devices that will solve various technical problems when medical devices are brought to the cloud, while Olympus will contribute to the establishment of an optimal network for the cloud endoscopy system and its reference model.
(1) NTT
NTT has been providing high-speed, low-latency networks to its customers and promoting the IOWN concept, including the IOWN APN, which connects sites with an extremely high-capacity end-to-end optical path. In this demonstration experiment, the IOWN APN technology is utilized to verify and optimize the network necessary for the cloud endoscopy system.
(2) Olympus
Olympus has the top market share in the global endoscope field and is promoting the concept of a cloud endoscopy system, in which the sophisticated functions of endoscopes are computed on the cloud. In this demonstration experiment, Olympus will provide the specific requirements and evaluation items for the cloud endoscopy concept, as well as the endoscopic equipment for the demonstration experiment.
Through this demonstration experiment, the two companies will confirm the feasibility of the cloud endoscopy system and help address social issues such as expanding access to advanced medical care. In addition, NTT will consider expanding use cases, such as promoting the use of other medical devices on the cloud, based on the knowledge gained from the demonstration experiment. Olympus will apply the results of this study and continue to study advanced technologies using IOWN technology, such as the cloud endoscopy system, that contribute to solving customer needs or problems.
1 Innovative Optical and Wireless Network (IOWN)
The IOWN is comprised of three components: the "All Photonics Network (APN)," which makes it possible not only for networks but also for terminal processing; the "Digital Twin Computing," which enables advanced and real-time interaction between objects and humans in cyberspace; and the "Cognitive Foundation," which efficiently deploys various ICT resources.
2 All Photonics Network (APN)
By introducing new optical technologies from the network to terminals and chips, APN achieves ultra-low power consumption and ultra-high-speed processing, which has been difficult to achieve. By assigning wavelengths to each function on a single optical fiber, we can provide multiple functions that support our social infrastructure, including information and communication functions such as the Internet and sensing functions, without interfering with each other.
3 Secure Optical Transport Network Technology
Technology for realizing secure information communication even in the age of quantum computers by sharing a common key between optical transmission devices using Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) and Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) and encrypting the communication with the key.


Contact Us
Tel: (+86) 400 610 1188
WhatsApp/Telegram/Wechat: +86 13621645194
Follow Us:




 Pharma Sources Insight January 2025
Pharma Sources Insight January 2025


