Shruti TalashiSeptember 14, 2023
Tag: GMP , QMS , Digitalization
Drugs that are available in the market should not deviate from its standardized quality parameters. All the drugs that are consumed by the humans are manufactured under guidelines provided by international and national drug regulatory bodies supervising and frequently auditing manufacturing plants where the products are assembled since these places should be maintain under a quality management system. In a company their quality management system is the internal reflection of external standards and known in short as QMS. QMS adds value to the organizations. International Standard Organization (ISO) 9001 defines quality management system (QMS) as a collection of rules, practices, and procedures used to guarantee that goods and services continually meet or surpass consumer expectations. How to use a quality management system to achieve long-term success is explained in ISO 9004. Guidance is provided by ISO 19011 for conducting internal and external audits. It is made with the intention of managing and enhancing quality in all facets of an organization's operations. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) is the foundation of one comprehensive model for an efficient pharmaceutical quality system that is described in international Council for Harmonization ICH Q10. Quality ideas are complemented by appropriate good manufacturing practice (GMP) laws.
QMS guidelines for the pharmaceutical industries are provided in the ICH Q10 that are adopted by the companies in order to achieve the standardization in the quality of production and product quality of the US FDA approved lifesaving drugs. Quality ideas are complemented by appropriate good manufacturing practice (GMP) laws. The relationship between pharmaceutical development and manufacturing activities should be strengthened by implementing ICH Q10 throughout the whole product lifecycle. The ICH was created in 1990 as a collaborative regulatory and industry endeavor to streamline the procedure for creating and registering new medicines in the US, Europe, and Japan. The guidelines made it possible to achieve global product quality harmonization for uninterrupted global pharmaceutical export. [1]
In the drug manufacturing industry, QMS is inevitable since the production of pharmaceuticals or biologics is a multi-step, complex process. It may be challenging to guarantee that all quality requirements are met due to its complexity. Numerous medications are made by multiple companies. These medications are known as generic medications and come in a variety of brand names. In terms of their active ingredients, dosage form, potency, mode of administration, safety, and efficacy, generic medications are identical to those sold under brand names e.g. Acetaminophen (Tylenol, Panadol), Aspirin, Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), Atorvastatin (Lipitor), Lisinopril (Prinivil, Zestril) and others. Similar with the biopharmaceutical medications or biologics which are distributed by multiple firms. These medicines are classified as biosimilars. In terms of safety, efficacy, and quality, biosimilars are comparable to name-brand biologics. They differ from biologics sold under a brand name though. Biosimilars may contain different inactive components and be produced utilizing a different manufacturing procedure e.g. Infliximab (Remicade, Inflectra, Renflexis), Adalimumab (Humira, Cyltezo, Abrilada), Rituximab (Rituxan, Rixathon, Truxima), Etanercept (Enbrel, Erelzi), Trastuzumab (Herceptin, Kanjinti, Ogivri) and others. A more recent class of medication, biosimilars are rising in popularity as the biosimilars market continues to grow, we can expect to see even more biosimilars available in the future. [2]
The production of pharmaceuticals is a multi-step, complex process. It may be challenging to guarantee that all quality requirements are met due to its complexity. Additionally in the pharmaceutical sector, fake medications are becoming more and more of an issue. These medications have the potential to be harmful and have negative effects on patients' health. To reduce the risk of fake medications entering the supply chain, QMSs was must to be created.
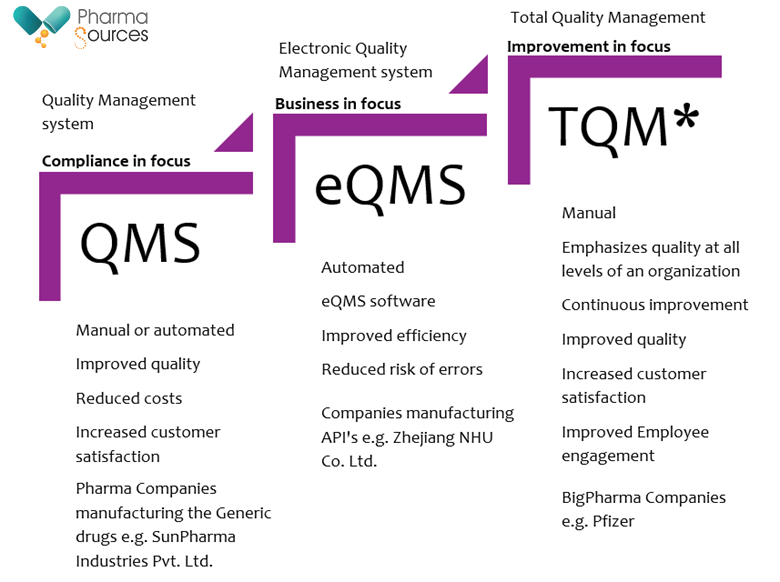
Figure showing a flowchart with the various forms of Quality management systems. About * 0.2% of the total existing global pharmaceutical companies are implementing the TQM approach of managing the health sector e.g. clinical research platforms, patient centric care services and these are the top 10 to 20 global bigpharma companies e.g. Pfizer, J&J, GSK, Sanofi & others.
Depending on the organization, different QMS, eQMS, and TQM implementation strategies will be used. However, each of the three strategically different approaches aims to assist companies in raising their standards of quality in line with company management team's interest and leadership. [3]
TQM will be a value added for the companies that are committed to the organizations continuous improvements. As compared to QMS and eQMS, there are more advantages of successfully implementing TQM which are listed as follows:
Enhanced product and service quality: TQM can assist businesses in locating and removing flaws in their goods and services. Improved client loyalty and satisfaction may result from this.
Cost savings: TQM can help businesses save money by reducing waste and boosting productivity. Profitability may increase as a result of this.
Increased employee morale: TQM can provide employees the freedom to take responsibility for their job. Employee productivity and morale may rise as a result. Most importantly the attrition rate is low and time invested in training the team is not wasted with loose the trained staff. It is not easy to keep everyone in the staff happy in the competitive market with all-time changing landscape in the pharma sector.
Increased customer satisfaction can be attained through TQM by offering clients goods and services that are in line with their requirements.
Market share growth: By offering goods and services that are better than those of the competition, TQM can assist businesses in gaining market share.
Most of the pharmaceutical industries are using the QMS that consists of four facets: Quality planning, Quality Assurance, Quality control and Quality improvement. This is distorted and more time consuming approach of maintaining the product quality. From a cultural, historical, geographical, and technological standpoint, collaboration and knowledge sharing across the whole lifecycle, from drug discovery to commercial manufacture, are extremely compartmentalized.
More trending is the enterprise recipe management (ERM) which are being adopted by pharma firms in order to speed up the process of maintaining the product life cycle from its synthesis, approval to manufacturing and marketing. It is not simple for a commercial pharma set up to adopt the digitalization of these process since it is cost, time & skills inclusive activities. But once the project is set off then the process of maintaining the quality compliance becomes much simpler than existing workflow. Hence this is worth investing in QMS makeover for pharma companies.
ERM enhances communication between process development and manufacturing facilities, allowing for quicker approval and introduction of novel medications. It can significantly shorten the time it now takes to transfer technology from a lab to a production line. Siemens is a global company likewise is AVEVA and Emerson process management companies that provides ERM services the digitalization of R&D and digitalization of manufacturing to pharma industry. A real enterprise recipe management strategy should do away with the need to manually transfer product data from one system and silo to another. Beginning with the development processes, it progresses to process optimization for manufacturing processes that are more standardized and manageable across nations, process machinery, or manufacturing locations. [4]
Leading the way in the deployment of digital technology has been Johnson & Johnson. The business has introduced a number of Industry 4.0 lighthouses, or industrial facilities that have undergone technological transformation. Johnson & Johnson has benefited from these lighthouses by increasing productivity, cutting expenses, and improving patient outcomes. Johnson & Johnson estimates that adopting digital technologies throughout its business has resulted in savings of $1 billion. Likewise, Pfizer has used digital technologies to improve its supply chain resilience, which has helped it to maintain production during the COVID-19 pandemic. AstraZeneca has reduced faults by 30% by using digital technologies to enhance the quality of its manufacturing procedures. [5]
The overall goal of strengthening the QMS with smarter digital tools is to enable greater enterprise-wide efficiency, productivity, and product quality as well as genuine agility that extends into the ecosystem. So with digitalization, Industry 4.0, and Pharma 4.0 all aid in the move to the digital pharmaceutical sector.
1) Igal Geiler, Sep 29th, 2022, QMS 101: Pharmaceutical Quality Management System, dotcompliance. https://www.dotcompliance.com/blog/pharmaceutical-manufacturing/pharmaceutical-quality-management-system/#
2) Bard, Google AI. Prompted "Any one drug produced by more than one company?" Bard, Google AI, 11 September at 14:03
3) Ida Gremyr, Jan Lenning, Mattias Elg and Jason Martin,' Increasing the value of quality management systems ' International Journal of Quality and Service Sciences Vol. 13 No. 3, 2021 pp. 381-394 Emerald Publishing Limited 1756-669X. DOI 10.1108/IJQSS-10-2020-0170
4) Christina Rucinski, April 7, 2022, Taking end-to-end Recipe Management in the Pharma Industry to the Next Level, SIMENS, https://blogs.sw.siemens.com/medical-devices-pharmaceuticals/2022/04/07/taking-end-to-end-recipe-management-in-the-pharma-industry-to-the-next-level/?ste_sid=4c56d07c3d921c5f5dc3ec7cd7a4c19e.
5) Bard, Google AI. Prompted 'please provide brief outcome of the statement below: Scale end-to-end adoption of digital and automation.' Bard, Google AI, 13 September 2023 at 14:59.
Ms. Shruti Talashi boasts a dual mastery of lab research and writing. Her doctoral study outcome as M.Phil in biomedical science while studying breast cancer and an extraordinary masters degrees dissertation work on exploring role of Gal-lectin in cancer metastasis fuels her extensive research interests. She has gained few publication in journals. Bridging the science-public gap is her passion, aided by expertise in diverse techniques. From oncology to antibiotic/drugs production, she's led and managed complex projects, even clinical trials. Now, as a freelance Content Coordinator for Sinoexpo Pharmasource.com, her industry knowledge shines through valuable insights on cutting-edge topics like GMP, QbD, and biofoundry.


Contact Us
Tel: (+86) 400 610 1188
WhatsApp/Telegram/Wechat: +86 13621645194
Follow Us:




 Pharma Sources Insight January 2025
Pharma Sources Insight January 2025


