Xiaomichong/PharmaSourcesSeptember 07, 2023
Tag: naringin , hesperidin , naringine
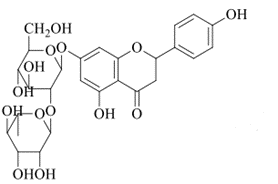
Naringin, also known as hesperidin or naringine, is a natural flavonoid compound. It is a colorless needle-shaped crystalline powder that is insoluble in cold water and extremely bitter in taste. Naringin is the main active ingredient in traditional Chinese medicines such as Gu Sui Bu, Zhi Shi, Zhi Qiao, and Hua JuHong. Modern pharmacological studies have found that naringin has various therapeutic effects, including anti-osteoporosis, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, anti-tumor, improvement of myocardial and liver injuries, and prevention and treatment of diabetes and its complications.
Naringin has significant advantages in the treatment of osteoporosis. It can inhibit the differentiation, proliferation, and bone resorption function of osteoclasts, and promote the expression of osteoblast marker proteins. It also inhibits the NF-κB and ERK signaling pathways induced by RANKL, which leads to abnormal osteoclast formation. Naringin can delay osteoporosis and promote the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts.
Naringin has shown certain effects against osteosarcoma, glioma, cervical cancer, colon cancer, lung cancer, thyroid cancer, and other tumor cells. Its mechanisms may include direct inhibition of tumor cell growth, proliferation, and migration, enhancement of the body’s immune response against tumors, synergistic enhancement of the activity of anti-tumor drugs, and reduction of tumor cell drug resistance.
Naringin has significant antioxidant effects and can protect against oxidative damage. It can scavenge free radicals such as DPPH, AAPH, and ABTS, inhibit the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and regulate the levels of various oxidative enzymes in the body.
Overall, naringin has diverse pharmacological properties and holds promise in various therapeutic applications.
Research has shown that naringin has good anti-inflammatory effects and can improve inflammation damage induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS), inhibit the protein and gene expression levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-8, and IL-1β in inflammation models, and reduce leukotriene B4 (LTB4) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) concentrations. It has also been found that the combined use of naringin and silk fibroin has a stronger inhibitory effect on related inflammatory factors than naringin or silk fibroin alone, indicating that the combination therapy of naringin and silk fibroin is of great significance in improving clinical efficacy, enhancing drug tolerance, and exerting optimal anti-inflammatory effects. In addition, other studies have shown that naringin can inhibit rheumatoid arthritis in rats by inhibiting IL-17, IL-10, and other related inflammatory factors in a dose-dependent manner. When the dosage of naringin is 200 mg/kg, it has significant inhibitory effects on osteoarthritis both in vitro and in vivo, and the mechanism is related to the antagonism of IL-1β, inhibition of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), and nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome signaling pathway.
Naringin has significant effects in the prevention and treatment of related pathogens. Research has found that the minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) of naringin against Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus sanguis, Streptococcus sobrinus, Actinomyces viscosus, Actinomyces naeslundii, and Lactobacillus acidophilus are 1, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 1, and 1 g/L, respectively. The minimum bactericidal concentrations (MBC) are 2, 1, 1, 1, 2, and 2 g/L, respectively. It has also been found that naringin can disrupt the normal growth, acid production, sugar production, and adhesion functions of the above pathogens. At the same time, research has shown that naringin has a time- and concentration-dependent inhibitory effect on Actinomyces viscosus and Porphyromonas gingivalis. In addition, comparing the combined therapeutic effects of naringin with antibiotics such as ciprofloxacin and tetracycline on the biofilm of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, it was found that naringin can enhance the therapeutic effects of ciprofloxacin and tetracycline on the biofilm of Pseudomonas aeruginosa compared to individual treatments.
Naringin has important value in the treatment of diabetes and its complications. Its mechanisms include: ① inhibiting ketoacidosis and lipid peroxidation; ② regulating the expression of TC, TG, and LDL-C proteins; ③ activating the AMPK-GLUT4 protein expression pathway, promoting glucose metabolism, reducing insulin resistance; ④ reducing extracellular matrix (ECM) accumulation, increasing MMP-2 expression; ⑤ reducing accumulation of free radicals, SOD, ROS, and CAT, inhibiting oxidative stress damage. Studies have shown that naringin can control renal functional disorders and the degree of injury caused by relieving oxidative stress induced by streptozotocin, inhibiting apoptosis induced by high glucose, and reducing the level of reactive oxygen species. The pharmacological effects of naringin on experimental type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in rats have also been shown to improve disrupted glucose and lipid metabolism, alleviate insulin resistance, enhance antioxidant capacity, and protect the liver.
Naringin has a certain improvement effect on common experimental myocardial injury in vivo and in vitro. Its mechanism is related to the regulation of apoptotic factors protein expression within cells by naringin, inhibition of protein phosphorylation in myocardial tissue, and blockade of the activation of the NF-κB inflammatory pathway after myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury (MI/RI) and hypoxia-reoxygenation injury (H/R) injury. Numerous studies have shown that naringin can improve MI/RI caused by various reasons. It not only inhibits the phosphorylation of NF-κB inhibitory protein α (inhibitor of NF-κBα, IκBα) in myocardial tissue, blocking the activation of the NF-κB pathway after MI/RI, but also improves the damage to H/R-type myocardial cell line H9c2 cells, and reduces the rate of cellular apoptosis. Another study has found that naringin can also improve H2O2-induced oxidative stress and high glucose-induced toxic damage to H9c2 cells by downregulating IL-6 and NF-κB protein expression levels.
Naringin has significant effects in the prevention and treatment of experimental liver injury, and has certain pharmacological effects. Its mechanism is significantly related to the ability of naringin to reduce CYP450 activity, inhibit phase I enzyme metabolism, promote phase II enzyme metabolism, and eliminate damage to liver cells caused by exogenous substances; it is also associated with the regulation of multiple intracellular oxidative enzyme content, inhibition of oxidative damage and apoptosis in liver cells, and further repair of damaged liver cells.
[1] Yang Xinrong, Dou Xia, Li Guofeng, et al. Research progress on the pharmacological effects and mechanisms of naringin [J]. Chinese Herbal Medicine, 2022,53 (10): 3226-3240
[2] Jin Yuanbao, Liu Ping, Liu Xiaogen, et al. Research progress on the biological activity of naringin [J]. Chinese Journal of Modern Medicine, 2018,20 (03): 92-97
Xiaomichong, a pharmaceutical quality researcher, has been dedicated to drug quality research and validation of drug analysis methods for a long time. Currently, he works for a large domestic pharmaceutical research and development company, engaged in drug inspection, analysis, and validation of analytical methods.


Contact Us
Tel: (+86) 400 610 1188
WhatsApp/Telegram/Wechat: +86 13621645194
+86 15021993094
Follow Us:




 Pharma Sources Insight January 2025
Pharma Sources Insight January 2025


