PharmaSources/Sha LuoDecember 10, 2021
Tag: Cyclodextrin , CD , glucose
Cyclodextrin (abbreviated as CD) is a type of macrocyclic molecules linked by glucopyranose units through α-1,4-glycosidic bonds. Among them, the most common cyclodextrins contain 6, 7 and 8 glucose units, which are called α, β and γ-cyclodextrins respectively. The space structure of cyclodextrin is similar to a truncated cone, and the hydroxyl group of the glucose monomer is exposed on the outside. This special molecular structure makes the cyclodextrin have the special properties of hydrophilic outer edge and the hydrophobic inner cavity. Fat-soluble drug molecules can bind to the hydrophobic cavity of cyclodextrin to form host-guest inclusion compounds, thereby improving drug solubility, enhancing drug stability, reducing toxic and side effects, improving drug bioavailability, and masking the body smell of drugs, etc. Therefore, it is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry.
However, natural CD has certain limitations in some aspects, such as low water solubility, high toxicity and unfavorable use, etc. Through alkylation, hydroxy alkylation or esterification of free hydroxyl groups in the structure by means of chemical modification and other means, it can synthesize CD derivatives with good water solubility, amorphous, high physical stability and low physiological toxicity to improve its application performance and application range. Hydroxypropyl CD, methyl CD and sulfobutyl CD are commonly used currently.
Drug solubilization: solubility is one of the important parameters of the drug itself. CD polymer materials can form inclusion compounds with some poorly soluble drugs to greatly increase their solubility. CD materials that improve drug solubility are mostly modified CD molecules with good water solubility.
Improvement of drug stability: the drug CD inclusion compounds can be considered as a "protective coat" of polymer materials built around the drug molecules, which prevents unstable drug molecules from being affected by the surrounding sensitive environment, and protects the drug from hydrolysis, oxidation, enzymatic hydrolysis, isomeric rearrangement, etc. The improvement of drug stability depends on the impact of drug groups embedded in the inner cavity of CD on the overall drug molecular stability, and it is closely related to the stability of the drug CD inclusion compound.
Reducing the toxicity and side effects: the drug-CD inclusion compound can reduce the dosage of the drug to a certain extent, thereby reducing the toxicity and side effects of the drug. The CD can inhibit drug crystallization and reduce tissue toxicity caused by drug crystallization in some cases. The CD can also reduce the damage of drugs to blood vessels by blocking the direct contact of drug molecules with epithelial cells of the blood vessel wall.
Improvement of drug bioavailability and taste masking: CD improves the bioavailability of drugs mainly based on the improvement of the solubility and dissolution of insoluble drugs, so as to promote the effective absorption of gastrointestinal tract. In addition, by forming inclusion compounds with drugs, CD can also mask the odor of drugs and inhibit the volatilization of drugs.
Natural α-CD and β-CD are the earliest CD materials used in pharmaceutical preparations and medical health supplies. The main functions of the CD in the listed preparations include solubilization, stabilization, promotion of dissolution, and masking the taste of the materials. For example, cefotiam hydrochloride tablets form a gel-like structure when exposed to water, which reduces the dissolution of the drug. After forming an inclusion compound with α-CD, α-CD can effectively inhibit the formation of gel and accelerate the dissolution of the drugs. Prostaglandin PGE2 is an oxytocin-like compound that can be used to help childbirth. However, PGE2 has poor chemical stability. Under certain circumstances, it is prone to hydrolyze, dehydrate or isomerize and lose its physiological activity. This shortcoming makes the administration route and application of prostaglandin PGE2 extremely complicated. β-CD was applied to the drug molecule of PGE2, which greatly enhances the stability of PGE2. A cyclodextrin drug, Prostarmon E, appeared on the Japanese market in 1976. Prostarmon E has shown many advantages when used in childbirth. It can be used in people who are not sensitive to oxytocin. It can also reduce the probability of bleeding after childbirth.
It is worth emphasizing that unmodified natural CD, especially α-CD and β-CD, are highly nephrotoxic when administered by injection, so most of them are used for oral and external preparations, and hardly used as preparation excipients for parenteral administration. Among the listed products, the pharmaceutical preparation PGE1-α-CD with α-CD as a stabilizer is approved for injection in cavernous body. The reason may be that the small amount of α-CD used in its prescription does not cause serious toxic and side effects.
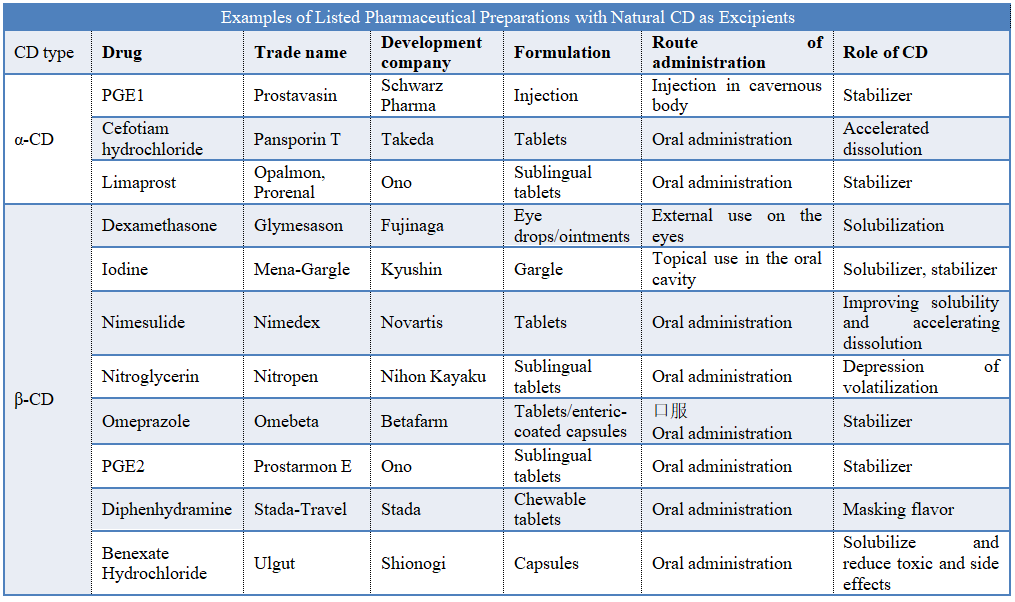
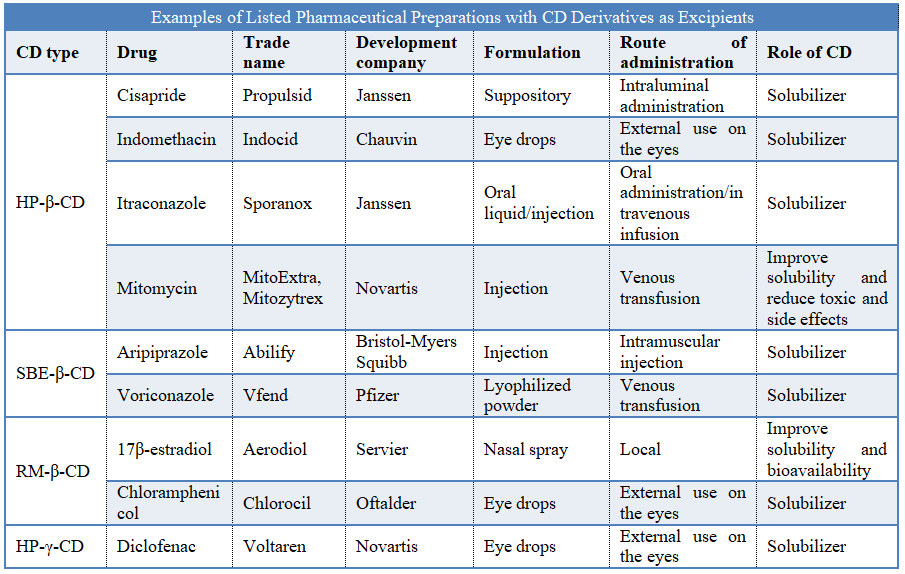
There are many types of modified CDs, and methylated-β-CD (RM-β-CD), hydroxypropyl-β-CD (HP-β-CD), SBE-β-CD, hydroxypropyl-γ-CD (HP-γ-CD), etc. are commonly used on the market currently. The main synthesis method is modified with C2-OH and C3-OH in the CD glucose monomer as the modification sites. HP-β-CD and SBE-β-CD are two injectable CD excipients that have been approved by the FDA. Compared with β-CD, HP-β-CD has high safety and strong water solubility, but its ability to include drugs decreases. The higher the degree of substitution of hydroxypropyl is, the weaker the inclusion ability will be. There is carboxyl in the structure of SBE-β-CD, so the interaction with the drug can be through hydrophobic interaction or electrostatic interaction between the drug and the material, and the water solubility is greatly improved due to the charge. So far, there are more than 10 preparations listed with modified CD as excipients, and the number is increasing continuously. Especially with injections, due to the excellent properties of modified HP-β-CD and SBE-β-CD, many injections and infusions have been approved to enter clinical practice.
The triazole antifungal drug voriconazole powder injection developed by Pfizer, with the trade name Vfend, was approved for marketing by the FDA in 2002. There are two formulations of voriconazole: oral preparation and injection. For general fungal infections, oral preparation of voriconazole will be used, but for some emergency patients or patients who cannot be administered orally, voriconazole injection has more significant efficacy. However, the solubility of voriconazole is low, only 0.2g·L-1 at pH3, and it is unstable in aqueous solution. At present, the commercially available Vfend uses SBE-β-CD as the solubilizer, co-dissolved with the main drug, voriconazole, and then lyophilized to form the powder injection. It will be reconstituted before use, which can solve the problems existing in the development of voriconazole injection well.
CD and its derivatives have unique excellent properties that can improve the solubility and stability of drugs, improve their bioavailability and reduce toxic and side effects. They have been used in dozens of listed preparations. However, problems such as its solubility and nephrotoxicity still limit the further application of such materials in certain aspects. Especially in the field of injection, the close attention shall be paid to the safety of CD excipients. Therefore, the modification and blending of such materials to improve water solubility and reduce toxicity are still the focus of research. In short, in some cases, CD has many advantages, and can replace toxic organic solvents and surfactants, and has a wide prospect of application.
[1] Qie Shuyan, Hao Ying, Liu Zongjian, Wang Jin, Xi Jianing. Research Progress of Cyclodextrin Polymer and Its Biomedical Application [J]. Acta Chemica Sinica, 2020, 78(03): 232-244.
[2] Qian Kang, Sun Haifeng, Ci Tianyuan, Ke Xue. Research Progress on the Application of Cyclodextrins in Listed Pharmaceutical Products [J]. Progress in Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2016, 40(07): 483-489.
About the author: Sha Luo, a worker for the R&D of traditional Chinese medicine, is now working in a large drug research and development company in China and dedicating to the R&D of new Chinese medicine.


Contact Us
Tel: (+86) 400 610 1188
WhatsApp/Telegram/Wechat: +86 13621645194
Follow Us:




 Pharma Sources Insight January 2025
Pharma Sources Insight January 2025


