PharmaSources/Sha LuoNovember 15, 2021
Tag: In-situ Gel , thermosensitive in situ gel , nanoemulsion in-situ gel
In-situ gel is a kind of liquid preparation, which will immediately transform to non-chemically crosslinked semisolid gel in the application site after administration. As a new formulation, in-situ gel has become one of the research hotspots in the field of preparation in recent years with huge potential in clinical application. Compared with common gel, in-situ gel has simple preparation technology. Before administration, in-situ gel is liquid preparation, which is convenient for administration with accurate dose. After administration, it will immediately transform to semisolid gel in vivo with long time residence in the application site and has good perform for sustained and controlled drug release. In addition, patients generally will not be uncomfortable after the use of this gel, representing its well acceptability and safety. In light of different formation mechanisms, in-situ gels can be divided into thermosensitive in situ gel, nanoemulsion in-situ gel and pH-sensitive in-situ gel.
Thermosensitive in situ gel: Thermosensitive in situ gel is made from thermosensitive polymers, which is in liquid below its lower critical solution temperature (LCST) and will be gelated when the ambient temperature reach or beyond LCST. It is the most widely studied and relatively mature sensitive gel at present. Matrix materials including poloxamer, chitosan, poly (N-isopropyl acrylamide) are common thermosensitive in situ gel.
Nanoemulsion in-situ gel: Nanoemulsion in-situ gel mainly uses the polymer solution formed by polysaccharide derivatives to undergo chemical reaction with a large number of cations such as K+, Na+, Ca2+ in the liquid environment in human body, and then undergo conformational change, thus forming gel at the application site. The commonly used materials are sodium alginate and deacetylated gellan gum.
PH-sensitive in-situ gel: PH-sensitive in-situ gel can receive or release protons from to the surrounding environment when the pH value of human body changes, which results in gelation reaction and slowly release drugs for a long time. The commonly used polymers include cellulose acetate phthalate, acrylic acid polymers (such as carbomer), chitosan and its derivatives.
Examples of in-situ gel preparations on the market
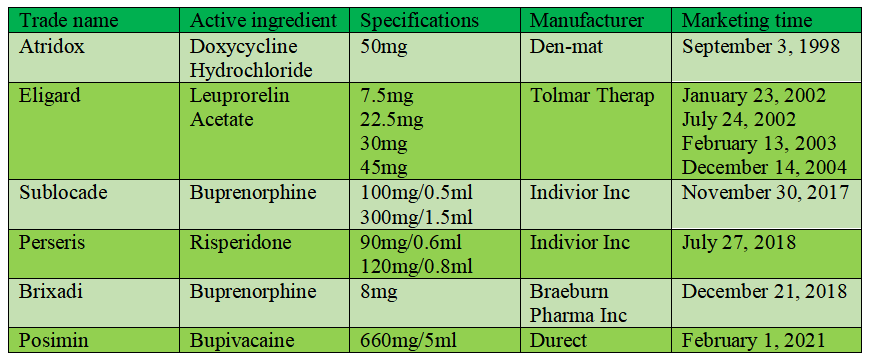
Atridox: Atridox is the first product approved for marketing with Atrigel technology. The product is light yellow or yellow viscous liquid. The preparation consists of 50mg doxycycline hydrochloride and 450mg polymer solution, which are packed in two syringes respectively. Before use, they are mixed evenly through an "axle tube", and then injected into the periodontal pocket of the patient with the needle, which can be continuously released in the periodontitis focus for one week. This product was listed abroad in 1998.
Eligard: Eligard (leuprorelin acetate) is a depot controlled release injection of luteinizing hormone releasing hormone (LHRH) agonist, which is used for palliative treatment of advanced prostate cancer. Eligard is a sterile suspension, which is prepared by Atrix Company's Atrigel drug sustained-release patented technology. It consists of two independent prefilled syringes, one of which is leuprorelin acetate powder, and the other is Atrigel system for reconstitution. After mixing and preparing the suspension within 30min before use, it was injected subcutaneously. After injection, NMP quickly diffuses into body fluid, and make the leuprorelin acetate loaded by PLGA become gel. Compared with the microsphere preparation of leuprorelin acetate, Eligard has a longer therapeutic effect with smaller dose. In December 2004, FDA approved the marketing of Eligard (45mg) of QLT Inc. of Canada, which was the first LHRH agonist approved by FDA to be used once every 6 months for the treatment of prostate cancer. Previously, several Eligard injections (with various specifications including 7.5mg, 22.5mg and 30mg) were approved for marketing.
Sublocade: The active ingredients in Sublocade are buprenorphine free base, partial agonist of opioid receptor and antagonist of opioid receptor, which are suitable for opioid dependence to help drug addicts gradually quit opioid drugs. In November 2017, FDA approved Indivior's Sublocade, which is an alternative adjuvant therapy that is expected to break the market balance. This product cannot only effectively help people get rid of opioid dependence, but also be injected subcutaneously once a month without the requirement of detoxification period. Therefore, Sublocade successfully overcome the medication limitations of other existing therapies.
Perseris: The active pharmaceutical ingredient of Perseris is risperidone. On July 27, 2018, FDA approved perseris extended-release suspension of Indivior for the treatment of schizophrenia in adults. Perseris is injected subcutaneously and delivers risperidone by extended-release delivery system to provide sustained levels of risperidone within one month. Perseris uses a sterile dual-syringe mixing system. One is a syringe containing the delivery system liquid composed of PLGH and NMP; and the another powder syringe is pre-filled with risperidone. Before use, liquid and powder are transferred back and forth between syringes with the connection. When the mixing cycle is finished, the mixture in the syringe is injected subcutaneously into the abdomen.
Brixadi: Braeburn Pharmaceuticals announced on December 23, 2018 that the tentative approval of Brixadi (long-acting buprenorphine) injected once a week (8, 16, 24, 32mg) and once a month (64, 96, 128mg), which is applied to treat moderate to severe use disorders of opioid, has been obtained from FDA. Brixadi is injected with a slender 23G needle into the buttock, thigs, abdomen or upper arm. In addition, Brixadi does not require refrigeration, thus reducing the cost of warehousing logistics. Brixadi has met all the necessary standards of quality, safety and efficacy, but due to exclusive considerations, the drug cannot be sold in the US market for the time being. At the end of November 2018, Brixadi was approved by the European Union and Australia to be listed under the brand name Buvidal, becoming the first long-acting drug for treating opioid dependence in these two markets.
Posimir: Posimir is a long-acting bupivacaine preparation developed with Saber technology, which can maintain local anesthesia for 72 hours and relieve the pains after surgery. On February 12, 2014, Durect received a complete reply letter from FDA on Posidur. FDA believes that there are not sufficient data on the safety of Posidur and the supplementary clinical trials are required. On November 11, 2014, FDA agreed to conduct only one additional clinical trial on soft tissue. In December 2015, Posidur was renamed Posimir and Phase III clinical trials were carried out. On May 8, 2017, Durect entered into a license agreement on the development and commercialization with Sandoz, a division of Novartis, with a total value of 293 million US dollars. Sandoz will obtain the development and marketing rights of Posimir of Durect in the United States. On February 27, 2019, Durect announced that it planned to submit a response to the complete reply letter of Posimir to FDA. On February 2, 2021, Durect announced that FDA had approved Posimir (Bupivacaine Solution) to be used in subacromial space under arthroscope, and easing the pain 72 hours after subacromial decompression under arthroscope.
As a new sustained-release drug delivery system, in-situ gel is still in its infancy, and there are still some problems to be solved. The most prominent problem the gel formed after injection because of physical or chemical transformation, and there are many problems in its transformation kinetics, especially the sudden release of drugs during the gelation. Another problem is that the shape of gel preparation after curing is not fixed, which will lead to poor uniformity of drug release rate and significant individual differences. Moreover, for new drug delivery technologies, the safety of polymers and the irritation of solvents have yet to be verified. From the perspective of industrialization, the ideal polymer materials are few in variety and high in price. The investment in R&D and the enlargement of the industrialization is vast. For thermosensitive hydrogels, the polymer degrades rapidly at normal temperature, which requires frozen storage. It is also a challenge to solve the problem of storage and cold chain pharmaceutical logistics at low temperature.
In-situ gel preparation is a promising drug delivery system, which is administered in liquid form with easy administration method and accurate dosage. After the gel is formed in situ, it can prolong the residence time of the drug in the body and release the drug continuously, and reduce the systemic absorption and toxicity through local action, which can improve the bioavailability and the therapeutic effect. In-situ gel is a new long-acting drug delivery system. With the continuous development of new technologies and biodegradable materials, there are more in-situ gel products on the market, and their unique advantages are increasingly attractive.
[1] Han Shengnan, Li Xixiang, Yan Zhipan, Zhang Zhirui. Research Survey of In-situ Gel [J]. Western Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 34(01): 153-157.
[2] Yang Boyuan, Chen Bin, Xu Peng, Wang Yanqing, Wang Tao. Development of In-situ Gel Technology and Research Progress of Related Products [J]. Chinese Journal of New Drugs, 2020, 29(17): 1964-1971.
[3] Zhang Yi, Li Pengyue, Xu Bing, Du Shouying. Research and Application Progress of In-situ Gel [J]. Journal of Liaocheng University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 33(05): 88-96.
About the author: Sha Luo, a worker for the R&D of traditional Chinese medicine, is now working in a large drug research and development company in China and dedicating to the R&D of new Chinese medicine.


Contact Us
Tel: (+86) 400 610 1188
WhatsApp/Telegram/Wechat: +86 13621645194
Follow Us:




 Pharma Sources Insight January 2025
Pharma Sources Insight January 2025


