PharmaSources/Professor in Medical FieldJune 16, 2021
Tag: SARS-CoV-2 , vaccine , COVID-19
Coronavirus is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus with a thick envelope, which has the largest genetic material among all the RNA viruses, and it is a key pathogen for many diseases of domestic animals, pets and human. It can cause various acute or chronic diseases. The common symptoms when people get infected with coronavirus include respiratory symptoms, fever, cough, shortness of breath and difficulty breathing. In more severe cases, the infection can even cause pneumonia, severe acute respiratory syndrome, renal failure and even death. In the research of SARS-CoV-2, also called COVID-19, everyone is discussing whether the vaccine against it is useful or not. For example, whether it can produce effective and sufficient antibodies. In this paper, we will talk about the effect of vaccine from a brand-new perspective - the size of SARS-CoV-2, and further discuss the reasons why antibodies produced after COVID-19 vaccine injection might be partially effective, ineffective or lose efficacy.
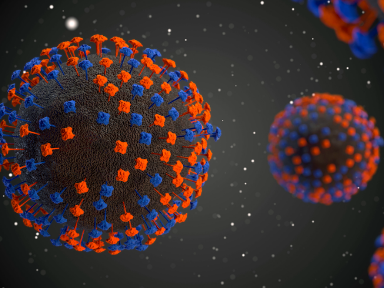
The initially measured and calculated size of SARS-CoV-2 is about 120-250 nanometers. However, SARS-CoV-2 is still constantly mutating and combining. Its new recombined genetic components and newly produced surface proteins might make its size bigger. At present, this known SARS-CoV-2 has a relatively larger size than other spherical RNA viruses. Comparing with the SARS virus, the SARS-CoV-2 is almost more than two times bigger than it. For example, the size of SARS virus is about 80-120 nanometers.
And the actual size of hepatitis B virus, is only about 40 nanometers. In contrast, SARS-CoV-2 is 3-7 times larger than hepatitis B virus. The size of a spherical virus we mentioned here usually refers to the diameter size of the largest cross-section of the sphere. If the maximum diameter of a spherical object is 3-7 times of another one, the surface areas of the larger one can be 10-50 times bigger than the other.
The most distinguished feature of SARS-CoV-2 is its corolla, which is caused by the convex protein it expresses. This protein actually increases the original volume of SARS-CoV-2 in a disguised way, especially when the virus contacts with the body fluid of the human body, its spherical external surface area will increase significantly. What's more, SARS-CoV-2 does not exist individually, but in a collective way. This movement pattern might make it not exist independently in the microstate, but gather into a cluster, which leads to the enlargement of its external surface area or size under the physiological conditions of human body in the real world.
Antibodies generally refer to those against xx proteins or molecules, but when it comes to SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, we will add the word "neutralizing". What does this stand for? Because there is a common misconception, which is most people think that antibodies kill virus by binding to virus, but that's not how neutralizing antibody works. The neutralizing antibody essentially realizes targeted binding to SARS-CoV-2. However, it generally can't kill virus specifically but just wrap it like a ball. In this way, the virus can be blocked from entering the cell. Then, the virus can be killed or the transmission can be blocked. There are many kinds of neutralizing antibodies, and generally they are mainly S protein against SARS-CoV-2.
Common neutralizing antibodies include igM and igG. Let's look at their differences. Immunoglobulin M (IgM) and immunoglobulin G (IgG) are antibodies or immune globulins produced by the immune system to fight against infection and to destroy antigens. IgM is a pentamer molecule that appears in the early period of infection and has 10 antigen-binding sites. IgG is a monomer molecule that appears in the later stage of infection and has two antigen-binding sites. IgM antibody immediately appears after human body gets infected, while IgG antibody appears only after IgM antibody disappears from the body a few days after infection. This is the key differences between IgM and IgG.
In addition, the basic structure of antibodies is the same. In simple terms, the antibody is made of two heavy chains (50 KD each) and two light chains (25 KD each), which are connected by disulfide bonds to form a Y-shaped structure (150 KD). Then, we can know that its volume is less than 0.2 cubic nanometers through conversion of 150KD, which means that the visual size of antibody is extremely small (<1nm) if the calculation is simplified as a sphere. What does this stand for? It means that plenty of antibodies have to bind to objects 150 to 850 times larger than them. In this case, it is like a regular ping pong ball compared with a basketball, and even a ping pong ball compared with a yoga ball at the maximum situation. The lack of specificity and the huge difference in volume might lead to poor efficacy of antibodies, or a large amount of antibodies are needed to completely eliminating viruses. However, human bodies cannot produce such huge amount of antibodies.
In short, the antibody will penetrate and crack the virus like a bullet if the antibody is specifically penetrating. However, in face of the SARS-CoV-2 with strong self-protection, the only way that antibodies can adopt is to wrap the virus body; but the antibodies produced by the vaccine may lose its efficacy when the number of antibodies produced by the human body is not sufficient or excessive number of SARS-CoV-2 is contacted from the outside world. Recent studies also show that vaccination cannot completely avoid the infection of new virus, but can avoid severe cases, which may mean that neutralizing antibodies offset the virulence of some SARS-CoV-2, but do not completely eliminate the viruses. In a word, this paper puts forward a possibility, which is the bulky size of SARS-CoV-2 is may be the reason why vaccine antibodies are ineffective. The research and development of COVID-19 vaccine still has a long way to go.


Contact Us
Tel: (+86) 400 610 1188
WhatsApp/Telegram/Wechat: +86 13621645194
+86 15021993094
Follow Us:




 Pharma Sources Insight July 2025
Pharma Sources Insight July 2025


