PharmaSources/CaicaiMay 31, 2021
Tag: Anlotinib , Sino Biopharmaceutical , Innovative drugs
Sino Biopharmaceutical has recently released its 2020 annual results, with total revenue of RMB23.647 billion, down 2.4% year on year, net profit attributable to the parent of RMB2.771 billion, up 0.3% year on year, net profit attributable to the parent of RMB3.114 billion excluding the impacts such as intangible assets amortization and convertible bond arising from the acquisition of Beijing Tide, decreased by 0.3% year on year, and R&D expenditure of RMB2.853 billion, accounting for 12.1% of the total revenue.
Sino Biopharmaceutical disclosed in a call meeting earlier that the sales of anlotinib in China were expected to reach RMB4-4.5 billion in 2020, which means that the blockbuster anlotinib contributed over 1/6 of the total revenue of RMB23.647 billion.
The Class 1 new drug anlotinib independently developed by Chia Tai Tianqing, a subsidiary of Sino Biopharmaceutical, was first approved in May 2018 for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who have undergone progression or recurrence after at least two lines of systemic chemotherapy and was subsequently approved for the treatment of soft tissue sarcoma, small cell lung cancer (SCLC), and medullary thyroid cancer.
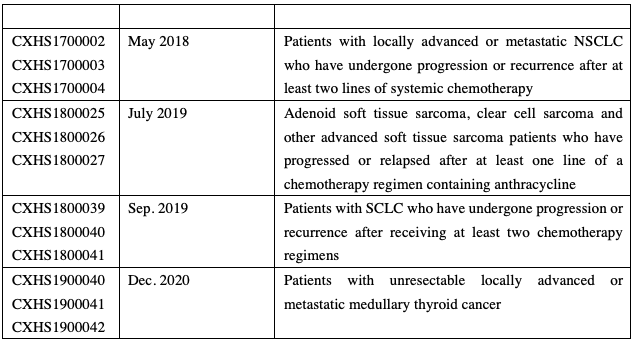
(Source: NMPA)
Anlotinib’s NSCLC indication was successfully included in the NRDL (National Reimbursement Drug List of China) in 2018; anlotinib was once again included in the NRDL in the new round of NRDL negotiations in 2020, with a price reduction by 37%, covering three indications: NSCLC, SCLC, and soft tissue sarcoma.
Chia Tai Tianqing is actively developing other indications for anlotinib, with a total of over 20 clinical trials underway. Among them, combination regimens of anlotinib and anti-PD-1/L1 drugs in development, which involve gastric cancer, liver cancer, and gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma, are already in Phase III clinical trials.
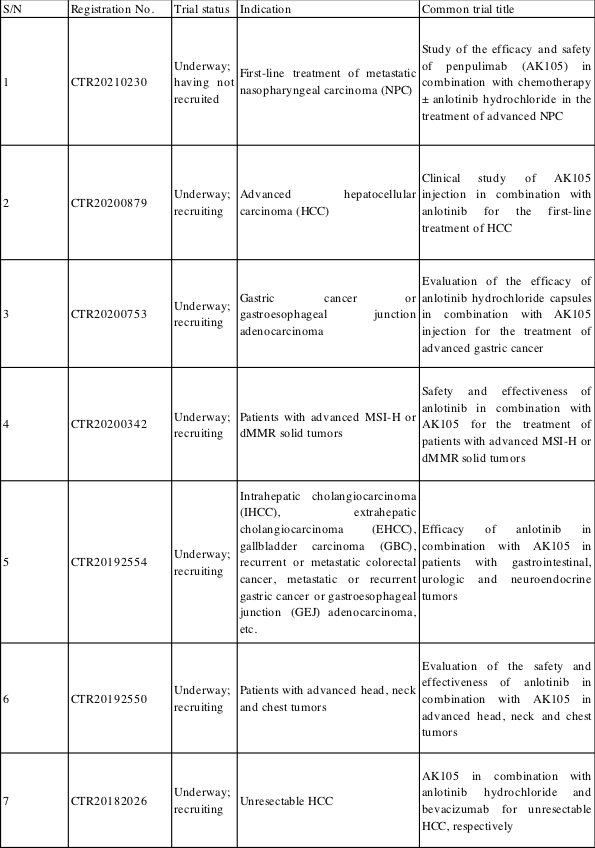
(Source: China Drug Clinical Trial Registration and Information Publicity Platform)
Undoubtedly, anlotinib will be a powerful growth engine for Sino Biopharmaceutical in the next three to five years. Then, with the full implementation of China’s centralized drug-procurement program, which will be the next innovative drug to be marketed by Sino Biopharmaceutical? Which will be the next blockbuster following anlotinib?
Sino Biopharmaceutical has now over 100 innovative drug varieties in development, with two marketed, three applied for production, and 33 in clinical stages. If you are looking for a professional bio pharmaceutical company in China, then Pharmasources would be your best choice.
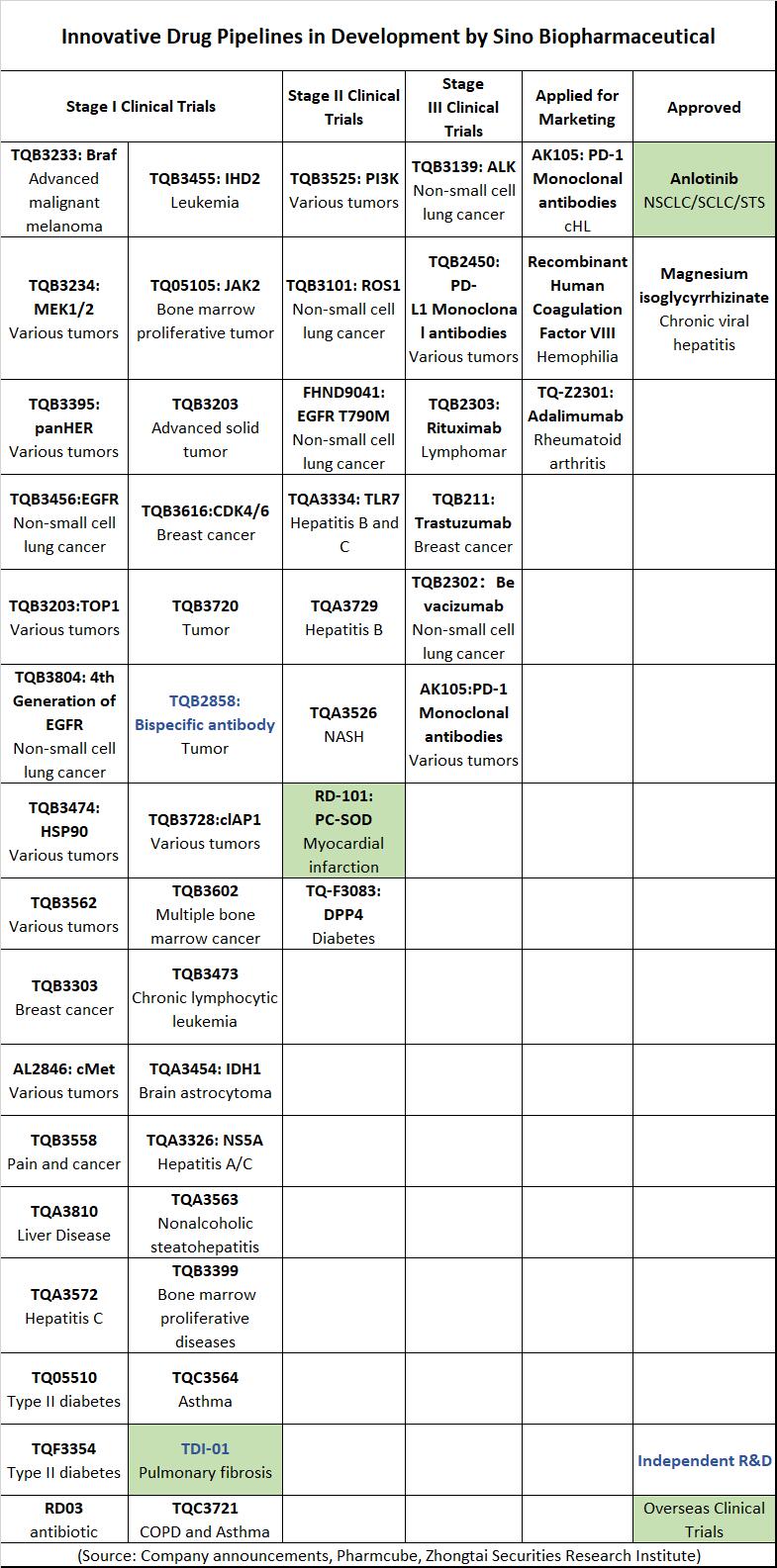
(Source: Company announcements, Pharmcube, Zhongtai Securities Research Institute)
Among the three drugs applied for marketing, AK105 and TQ-Z2301 are not considered to be Sino Biopharmaceutical’s own innovative drugs. AK105 is an anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody independently developed by Akeso, and Chia Tai Tianqing only has exclusive sales rights for AK105 in China. TQ-Z2301 is an adalimumab biosimilar. Only the recombinant human coagulation factor VIII for the treatment of Hemophilia A is considered to be Sino Biopharmaceutical’s own innovative drug and is expected to be approved for marketing this year, however, it is unlikely to become a blockbuster due to the restricted indication for the treatment of hemophilia A.
Besides these three applied for marketing, anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody TQB2450, ALK inhibitor TQB3139, and ROS1 inhibitor TQB3101 are expected to be approved for marketing in 2022, and PI3K inhibitor TQB3525 is expected to be approved for marketing in 2023.
Among them, the ALK inhibitor TQ-B3139 has the fastest progress, with a phase III clinical study of TQB3139 in combination with crizotinib in NSCLC initiated in 2019, and the drug is expected to be the first innovative drug applied for production.
Four ALK inhibitors have been approved in China, namely Pfizer’s crizotinib (Jan. 2013), Novartis’ ceritinib (May 2018), Roche’s alectinib (Aug. 2018), and Betta Pharmaceuticals’ ensartinib (Nov. 2020), with only ensartinib being the Chinese-produced drug, however, the sales of these drugs are lackluster, and it remains to be seen how the subsequent results of Betta’s ensartinib will be.
As for PI3K inhibitors, several have been approved worldwide, however, none have been approved in China. Among them, Bayer’s copanlisib has been applied for marketing in China, while Novartis’ alpelisib and Roche’s GDC-0077 are in the Phase III clinical stage.
Furthermore, no Chinese-produced anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody has been approved, therefore, there is still some market space for the anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody TQB2450. CDK4/6 inhibitors such as TQB3616 will also be applied for approval and production in succession.
The author holds that it is unlikely that Sino Biopharmaceutical will have another blockbuster like anlotinib in the next three to five years, however, its products will be like ‘hundred flowers in bloom’ in Chinese. By then, the marketing of ALK inhibitor, PI3K inhibitor, ROS1 inhibitor, CDK4/6 inhibitor and other innovative drugs will greatly enrich the innovative drug pipelines of Sino Biopharmaceutical and together become the future growth engine of Sino Biopharmaceutical.
Caicai, a Master of Pharmacy from Shanghai Jiaotong University, used to work in the Institute of Science and Technical Information. Currently as a practitioner in the drug surveillance system, she is good at interpreting industry regulations, pharmaceutical research developments, etc.


Contact Us
Tel: (+86) 400 610 1188
WhatsApp/Telegram/Wechat: +86 13621645194
Follow Us:




 Pharma Sources Insight January 2025
Pharma Sources Insight January 2025


