PharmaSources/CaicaiNovember 10, 2020
Junshi Biosciences was officially listed on the SSE STAR Market on July 15, with the stock code: 688180 and the issue price at RMB55.5/share; the opening price surged by nearly 200%, with the market value peaking at more than RMB150 billion. The stock price slightly fell in the following days, with the closing price reaching RMB111.65/share on July 20 and the market value reaching RMB97.278 billion, still approaching RMB100 billion.
There are often such cases as making a great fortune overnight by going public in the biotech industry in recent years. BeiGene, Innovent, Junshi, and Henlius have been called “four little biotech kings of H shares” by the industry media, common grounds are that founders aged about 50 in the prime of life, international executive management teams, more courageous R&D investment and overseas clinical trial strategies, and crossover teams familiar with entrepreneurship and capital market.
Among those four bio pharmaceuticals companies, BeiGene mainly focuses on technologies in small molecule targeted drugs instead of monoclonal antibodies, while Henlius’ R&D focus is on the layout of biosimilar drugs. Junshi and Innovent resemble each other most: first products marketed by them were both anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibodies, and their layout focuses in the next 3-5 years areto develop new indications of anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibodies.

From “surprisingly synchronizing” to “differentiating”
Innovent was founded in Suzhou in Aug. 2011 and listed on HKEx’s Main Board in Oct. 2018; Innovent’s anti-PD-1 sintilimab (trade name: TYVYT) was offically approved in Dec. 2018 for the third-line treatment of classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma and become the second Chinese-produced anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody approved; Innovent’s bevacizumab biosimilar (trade name: BYVASDA) was officially approved in China in June 2020 to become the second variety marketed of Innovent.
Junshi Biosciences was founded in Shanghai in Dec. 2012 and listed on HKEx’s Main Board in Dec. 2018; Junshi Biosciences’ anti-PD-1 toripalimab (trade name: Tuoyi) was approved for marketing in China in Dec. 2018 for the second-line treatment of melanoma and become the first Chinese-produced anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody marketed.
Therefore, except for one year apart in their founding, Innovent and Junshi were keeping in step, however, with the differences in the new indication layout of their anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibodies and the marketing of Innovent’s bevacizumab, the business development of Innovent and Junshi will be different and this trend will enlarge.
Differences in the R&D pipeline and business strength, etc. will decide which will go further in the future.
Comparison of business performance
Innovent: Its revenues from 2017 to 2019 were separately RMB19 million, RMB9.5 million, and RMB1.048 billion. The reason for the sharp increase in the revenue in 2019 was the same to Junshi: the marketing of an anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody. The sales of sintilimab reached RMB1.016 billion in 2019.
Junshi Biosciences: Its revenues from 2017 to 2019 were separately RMB54 million, RMB3 million, and RMB775 million, with a compound annual growth rate of 278.8%, and net profits attributable to the owners of the parent company being separately RMB-317 million, RMB-723 million, and RMB-747 million.
Innovent and Junshi generated income mainly depending on the business other than their core pharmaceutical product before 2019, which was low. The reason for the sharp increase in their revenue in 2019 was the marketing of the anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibodies. The net profits of both pharmaceutical enterprises were negative and their losses tended to expand mainly because of the clinical study expenses that still could not be temporarily covered by sales revenue.
The sales of sintilimab were RMB200 million more than the sales of toripalimab because the Hodgkin’s lymphoma indication covers more patients than melanoma indication of Junshi. Plus, sintilimab became the only anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody that was included in the NRDL (National Reimbursement Drug List of China) in Dec. 2019, giving it more competitive edges. Sintilimab’s new indication for the first-line treatment of non-squamous NSCLC in combination with chemotherapy has been applied for marketing in Apr. 2020; toripalimab’s new indications for the third-line treatment of nasopharyngeal cancer and second-line treatment of urothelial carcinoma have also been applied for marketing in May 2020; Innovent’s bevacizumab was approved for marketing in June 2020. It is still hard to tell how the performance of the two company will be with the approval of the new indications of their anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibodies and the approval of Innovent’s 2nd variety.
Comparison of R&D pipelines
Innovent: Innovent now has 21 new drug varieties covering disease areas including oncology, metabolic diseases, and autoimmune, etc.; wherein, 16 varieties have entered clinical studies, including 4 varieties in phase III clinical studies, 2 biosimilars have been filed NDAs and included in the priority review, and 2 products have been approved for marketing, respectively sintilimab (trade name: TYVYT) and bevacizumab biosimilar (trade name: BYVASDA).
The R&D pipelines of Innovent are based on innovative oncology drugs, and the strategy is to spread risks by choosing drug targets: Innovent’s candidate drugs closest to marketing are biosimilars or drugs of which the targets (PD-1, PCSK9, OX40) are sufficiently studied, accounting for 55% of its R&D pipelines; drugs in early clinical phases with new targets, such as CTLA-4, RANKL, and CD47, and bispecific antibody varieties developed centering on PD-1/PD-L1, etc. have high R&D risks, however, once successfully developed, they have the potential to become first-in-class.
Junshi Biosciences: Junshi now has 21 products in development, including 13 original new drugs in independent development and 8 in development with partners; wherein, 1 variety (toripalimab) has been marketed, 1 variety (UBP1211) has been filed NDA and accepted, and IND applications of 9 varieties have been approved.
Junshi mainly adopts the fast-follower strategy in new drug R&D. It fast follows and develops drugs with targets such as PD-(L)1, PCSK9, and IL17A, and focuses on developing the indications of core products such as toripalimab in China. Its subsequent strategy is to develop first-in-class drugs, the representative varieties are anti-BTLA monoclonal antibody (JS004) and COVID-19 neutralizing antibody (JS016). In particular, JS016 is co-developed by Junshi and Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Phase I clinical trial of JS016 was initiated on June 7 and the subject enrollment was completed on July 13. The drug, if successfully marketed, will greatly promote the growth of Junshi.
R&D pipelines of Junshi
Overall, some pipelines of Innovent and Junshi coincide with each other. Besides its anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody, the 2nd variety of Junshi Biosciences expected to be marketed is also a biosimilar, an adalimumab biosimilar. Furthermore, Junshi is also developing drugs with targets that are hot in the world: PCSK9, PI3K-α, and TIGIT, etc. However, the two enterprises are not identical, for example, Innovent is developing the drug with CD47 target, which Junshi is not developing, while Junshi is developing the drug with BLyS target, which Innovent is not developing.
What is the most important for Innovent and Junshi in the next 3 to 5 years is to expand the new indications of their own anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody.
Strategies for the anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody market
Junshi adopts the market development strategy of “fast marketing” with “small indication + big indication”. The objective of fast marketing for toripalimab is achieved through the “green channel”: priority review upon its indications which has the advantage of catering to urgent clinical needs. That is to say, Junshi first expands toripalimab’s indications for the treatment of melanoma, nasopharyngeal cancer and urothelial carcinoma that share relatively small patient groups and while conducting the clinical trials of indications such as lung cancer, liver cancer, esophagus cancer and breast cancer, etc. which share large patient groups to drive the market development of big indications.
Innovent adopts the development strategy of “fast marketing” with “big indication”. Sintilimab was first marketed for the treatment of Hodgkin’s lymphoma, and the drug was applied for a new indication for the first-line treatment of non-squamous NSCLC in combination with chemotherapy this April. Innovent leads the market in China in the clinical trial progress of big cancer types such as NSCLC, liver cancer, and gastric cancer.
Indication Layout of Anti-PD-1 Monoclonal Antibodies Marketed in China
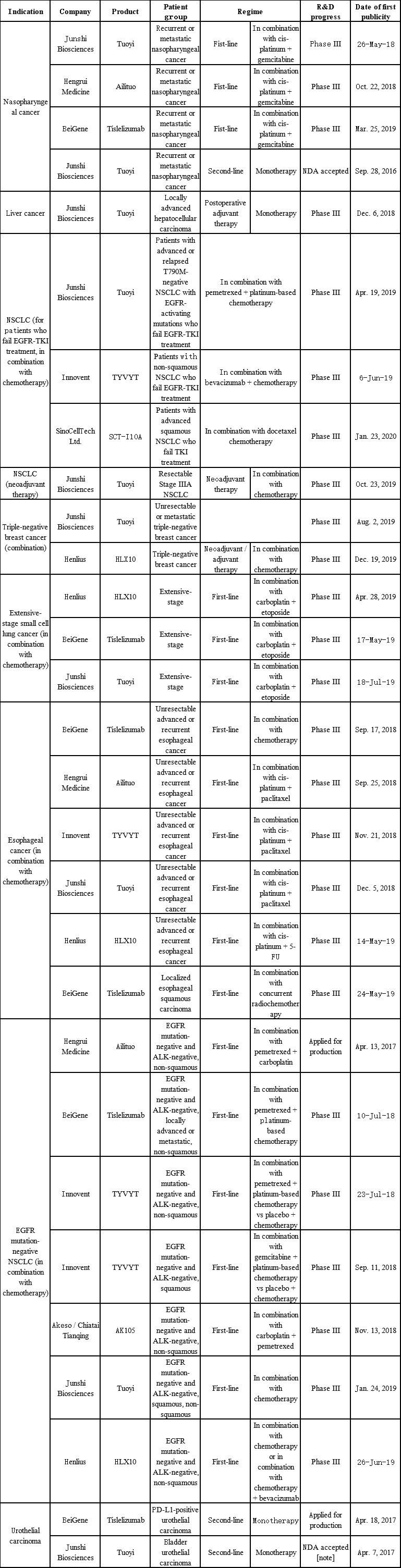
(Source: China Drug Clinical Trial Registration and Information Publicity Platform, company prospectuses)
The overall cancer incidence is on the rise in China, and the number of new cancer patients will increase year by year. Lung cancer, liver cancer, gastric cancer, colorectal cancer, and breast cancer are the top five types of cancer with high incidence. The total incidence of these five types of cancer accounted for more than 50% of the overall cancer incidence in China in 2018. The layout of big indications will increase the sales of anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibodies once the indications are approved.
Comparison of R&D investment
The R&D investment of Junshi Biosciences from 2017 to 2019 was respectively RMB275 million, RMB538 million, and RMB946 million, growing by 95.64% and 75.84% year on year, while, the R&D investment of Innovent from 2017 to 2019 was respectively RMB350 million, RMB1.22 billion, and RMB1.29 billion, growing by 248.6% and 5.7% year on year. Currently, the R&D investment of Innovent is more than that of Junshi because the two have different development strategies: most products of Junshi are independently developed, therefore, its R&D expenses are generally spent on clinical trials, while in addition to this part, Innovent also has expenses resulting from new product introduction.
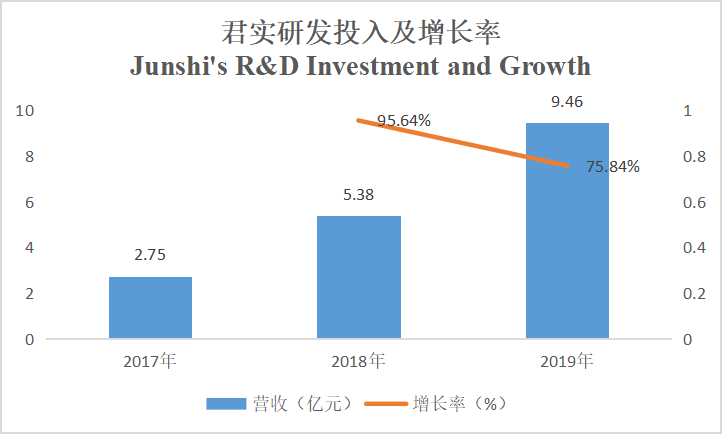
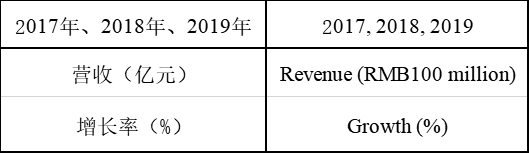
(Source: Company annual reports)
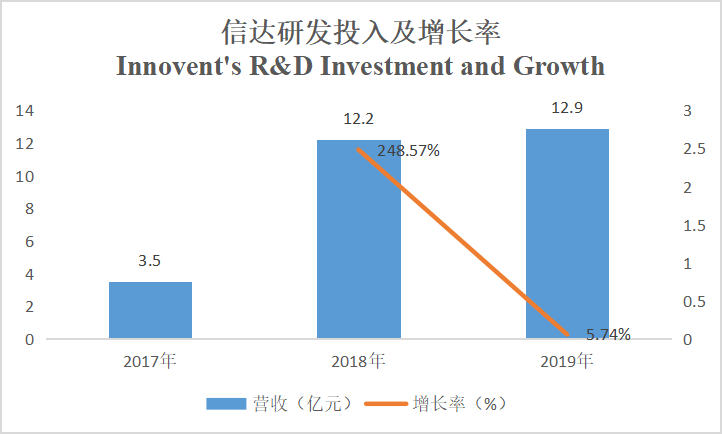
(Source: Company annual reports)
Junshi Biosciences has three R&D centers in Suzhou, San Francisco, and Maryland and two production bases in Wujiang, Suzhou, and Lingang, Shanghai. The bases use the internationally advanced single-use production technology for the whole process, with fermentation production capacity separately expanding to 3,000L and 30,000L. The base in Wujiang has obtained the Pharmaceutical Production License; the base in Lingang (Phase I covers an area of 80mu and has a floor area of about 70,000m2) is under fast construction.
Innovent has established a high-end biological drug industrialization base, with a floor area of 93,000m2, and the industrial production line has been constructed according to the GMP requirements of the NMPA, the FDA, and the EMA.
Comparison of development strategies
The differences between Junshi and Innovent specifically reflect the two different pharmaceutical enterprise strategies: valuing independent R&D over the speed or valuing the speed over independent R&D. At the moment, Junshi values the exploration of a core technology system more, while, Innovent directly introduces technology licensing externally to achieve fast development of products.
Junshi possesses a relatively complete technology system for innovative monoclonal antibody drugs. Toripalimab is the first Chinese-produced anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody marketed in China, and more importantly, it was independently developed by Junshi that got involved in the whole process including the key link of monoclonal antibody design.
We can see indirectly from the reserve of patents that the independent R&D ability of a company is strong if most of the patent inventors are members of the company.
From the perspective of patent inventors, Junshi’s core team members including Dr. Yao Sheng, Dr. Wu Hai, Dr. Feng Hui, and Dr. Chen Bo have been deeply involved in the company’s R&D and are truly core R&D personnel.
Innovent is keener on bringing in varieties and technologies externally to rapidly advanced pipeline development and commercialization. From the perspective of R&D pipelines, many varieties of Innovent are products developed through technologies introduced, however, Innovent’s independent R&D ability may be improved with the joining of Liu Junjian, Ph.D., in 2015.
Summary
Overall, Innovent’s revenue exceeded that of Junshi’s in 2019, and Innovent’s anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody is ahead of Junshi’s in the layout of big indication. With two products marketed, Innovent’s revenue is likely to also exceed that of Junshi’s in 2020. However, Junshi has strong independent R&D abilities and has been able to independently develop an anti-BTLA monoclonal antibody (approved for clinical trials in China and the U.S.) that is first-in-class. Therefore, which will go further in the future remains to be seen.
However, what is certain is that strong R&D pipelines and excellent development strategies will influence the future of pharmaceutical enterprises.
Caicai, a Master of Pharmacy from Shanghai Jiaotong University, used to work in the Institute of Science and Technical Information. Currently as a practitioner in the drug surveillance system, she is good at interpreting industry regulations, pharmaceutical research developments, etc.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Editor's Note:
To become a freelance writer of PharmaSources.com,
welcome to send your CV and sample works to us,
Email: Julia.Zhang@imsinoexpo.com.


Contact Us
Tel: (+86) 400 610 1188
WhatsApp/Telegram/Wechat: +86 13621645194
Follow Us:




 Pharma Sources Insight January 2025
Pharma Sources Insight January 2025


