October 21, 2020
Tag:
In organic chemistry, peptide synthesis is the production of peptides, which are compounds that link multiple amino acids through amide bonds (also known as peptide bonds).The peptide is chemically synthesized by the condensation reaction described by carboxyl groups of one amino acid of another.Protective group strategies are often required to prevent undesirable side reactions with various amino acid side chains.The most common method of chemical peptide synthesis is to start with the carboxyl end (C-terminal) of the peptide and then proceed to the amino end (N-terminal).Protein biosynthesis (long peptides) in living organisms occurs in the opposite direction.
Chemical synthesis of peptides can be performed using classical solution-phase techniques, although it has been replaced by solid-phase methods in most research and development settings (see below).However, solution phase synthesis retains its usefulness in the large-scale production of industrially produced peptides.
Chemical synthesis promotes the production of peptides that are difficult to express in bacteria, incorporation of unnatural amino acids, modification of the peptide/protein backbone, and synthesis of D proteins composed of D-amino acids.
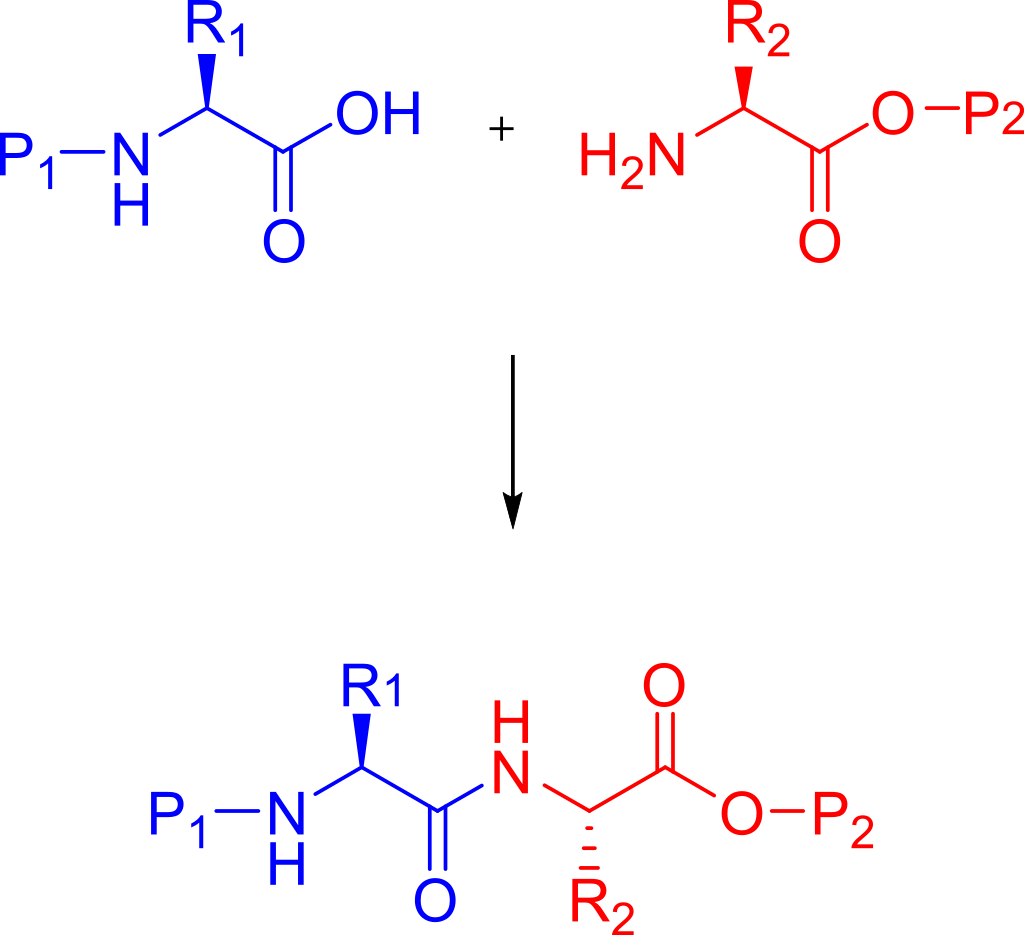
The methods established in the laboratory to produce synthetic peptides are called solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS).Pioneered by Robert Bruce Merrifield, SPPS can rapidly assemble peptide chains through continuous reactions of amino acid derivatives on insoluble porous supports.
Solid supports consist of small polymeric resin beads that are functionalized by reactive groups (e.g., amines or hydroxyl groups) linked to the nascent peptide chain.Since the peptide remains covalently linked to the carrier throughout the synthesis process, excess reagents and by-products can be removed by washing and filtration.This method avoids the relatively time-consuming separation of product peptides from solution after each reaction step, which will be necessary when using conventional solution-phase synthesis.
Appropriate protecting groups (e.g., Boc (acid-labile) or Fmoc (base-labile)) must be used to protect each amino acid to be coupled at the N-terminal and side chains of the peptide segment, depending on its side chain and amino acid.The protection strategy used (see below).
The general SPPS procedure is one of the repeated cycles of alternating N-terminal deprotection and coupling reactions.The resin can be washed between each step.First, amino acids are coupled to resins.Subsequently, the amine is deprotected and then coupled to the free acid of the second amino acid.The cycle was repeated until the desired sequence was synthesized.The SPPS cycle can also include capping steps to prevent the end of unreacted amino acids from reacting.At the end of the synthesis, the crude peptide is cleaved off the solid support while all the protecting groups are removed using reagent strong acids such as trifluoroacetic acid or nucleophiles.Crude peptides can be precipitated from non-polar solvents such as ether to remove organic soluble by-products.Crude peptides can be purified using reversed-phase HPLC.Purification processes, especially those for longer peptides, can be challenging because a small number of by-products that are very similar to the products must be removed.Therefore, so-called continuous chromatography, such as MCSGP, is increasingly used in commercial environments to maximize yield without sacrificing purity.
SPPS is limited by the yield of the reaction, and generally peptides and proteins in the 70 amino acid range are pushing the limits of synthetic accessibility.The difficulty of synthesis also depends on the sequence; in general, sequences that are prone to aggregation, such as amyloid, are easily produced.Longer lengths can be obtained by using ligation methods such as natural chemical ligation, where two shorter fully deprotected synthetic peptides can be linked together in solution.
If the original article is reprinted, please indicate the source( www.gotopbio.com )”


Contact Us
Tel: (+86) 400 610 1188
WhatsApp/Telegram/Wechat: +86 13621645194
Follow Us:




 Pharma Sources Insight January 2025
Pharma Sources Insight January 2025


